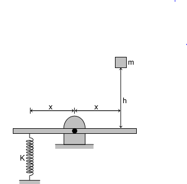
A crate of mass m falls from a height $h$ onto the end of a platform, as shown in the figure. The spring is initially unstretched and the mass of the platform can be neglected. What will be the maximum elongation of the spring assuming that there is no loss of energy,

Important Questions on Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion
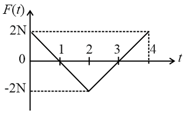
[Take ]
Two particles of masses move with initial velocities and . On collision, one of the particles get excited to higher level, after absorbing energy If final velocities of particles be and then we must have:
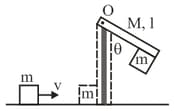
A block of mass slides with velocity on a frictionless horizontal surface and collides with a uniform vertical rod and sticks to it as shown. The rod is pivoted about and swings as a result of the collision making angle before momentarily coming to rest. if the rod has mass and length the value of is approximately