A cricket bat strikes a ball of mass travelling towards it. The ball initially hits the bat at a speed of and returns along the same path with the same speed. The time of impact is . You may assume no force is exerted on the bat by the cricketer during the actual collision.
(a) Determine the change in momentum of the cricket ball.

Important Questions on Momentum
A cricket bat strikes a ball of mass travelling towards it. The ball initially hits the bat at a speed of and returns along the same path with the same speed. The time of impact is . You may assume no force is exerted on the bat by the cricketer during the actual collision. Determine the force exerted by the bat on the ball.
A cricket bat strikes a ball of mass travelling towards it. The ball initially hits the bat at a speed of and returns along the same path with the same speed. The time of impact is . You may assume no force is exerted on the bat by the cricketer during the actual collision.Describe how the laws of conservation of energy and momentum apply to this impact and state whether the impact is elastic or inelastic.
State the principle of conservation of momentum and state the condition under which it is valid.
An arrow of mass is fired horizontally towards an apple of mass that is hanging on a string, as shown in Figure. The horizontal velocity of the arrow as it enters the apple is . The apple was initially at rest and the arrow sticks in the apple. Calculate the horizontal velocity of the apple and arrow immediately after the impact.
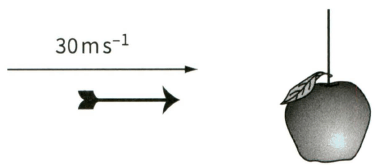
An arrow of mass is fired horizontally towards an apple of mass that is hanging on a string, as shown in Figure. The horizontal velocity of the arrow as it enters the apple is . The apple was initially at rest and the arrow sticks in the apple.Calculate the change in momentum of the arrow during the impact.
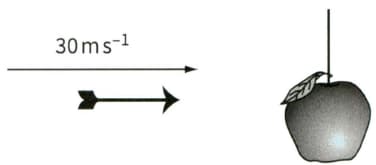
b An arrow of mass is fired horizontally towards an apple of mass that is hanging on a string, as shown in Figure. The horizontal velocity of the arrow as it enters the apple is . The apple was initially at rest and the arrow sticks in the apple.Calculate the change in total kinetic energy of the arrow and apple during the impact.
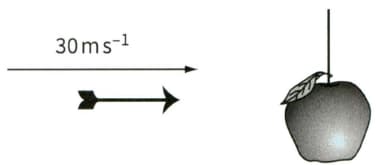
b An arrow of mass is fired horizontally towards an apple of mass that is hanging on a string, as shown in Figure. The horizontal velocity of the arrow as it enters the apple is . The apple was initially at rest and the arrow sticks in the apple.
(iv) A rubber-tipped arrow of mass is fired at the centre of a stationary ball of mass . The collision is perfectly elastic. Describe what happens and state the relative speed of separation of the arrow and the ball.
State what is meant by a perfectly elastic collision.
