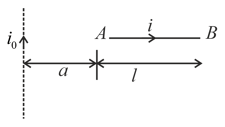
A finite conductor carrying current is placed near a fixed very long wire current carrying as shown in the figure. Find the point of application and magnitude of the net ampere force on the conductor . What happens to the conductor if it is free to move. (Neglect gravitational field)


Important Questions on Magnetic Effect of Current
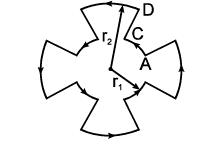
A current of flows around a closed path in a circuit which is in the horizontal plane. The circuit consists of eight alternating arcs of radii and . Each arc subtends the same angle at the centre.
(i) Find the magnetic field produced by this circuit at the centre.
(ii) An infinitely long straight wire carrying a current of is passing through the centre of the given circuit vertically with the direction of the current being into the plane of the circuit. What is the force acting on the wire at the centre due to the current in the circuit? What is the force acting on the arc and the straight segment due to the current in the central wire.
A rectangular loop made from a uniform wire has length , width and mass . It is free to rotate about the arm , which remains hinged along a horizontal line taken as the -axis as shown in figure.Take the vertically upward direction as the axis. A uniform magnetic field exists in the region. The loop is held in the plane and a current I is passed through it. The loop is now released and is found to stay in the horizontal position in equilibrium.
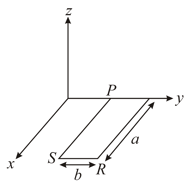
(a) What is the direction of the current in ?
(b) Find the magnetic force on the arm .
(c) Find the expression for in terms ofand .
A ring of mass and radius is rotated in uniform magnetic field which is perpendicular to the plane of the loop with constant angular velocity . Find the net ampere force on the ring and the tension developed in the ring if there is a current i in the ring. Current and rotation both are clockwise.
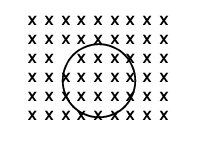
A long non-magnetic cylindrical conductor with inner radius a and outer radius carries a current . The current density in the conductor is uniform. Assume end effects can be neglected.
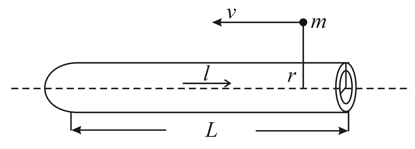
(a) Prove by the Biot-Savart law that the magnetic field, if any, at a point is always tangential to the circle passing through the point, with the centre of the circles on the axis of the cylinder.
(b) Find the magnetic field due to the current as a function of radius.
(i) inside the hollow space (ii) within the conductor (iii) outside the conductor
(c) A beam of particles, each with positive charge and mass travels with initial velocity anti-parallel to the direction of the current. Assume that the length of cylinder is . Find the deflection of a particle as a function of its initial distance r from the axis if when it goes from one end to other end. You can assume that the velocity is high enough such that the velocity is constant and the deflection is small.
