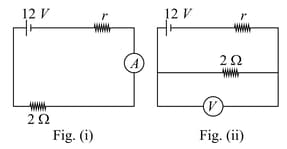
A galvanometer (coil resistance ) is converted into a ammeter using a shunt of and connected as shown in the figure (i). The ammeter reads . The same galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter by connected a resistance of in series. This voltmeter is connected as shown in figure (ii). Its reading is found to be of the full scale reading. Find range of the ammeter and voltmeter.


Important Questions on Current Electricity
A galvanometer (coil resistance ) is converted into a ammeter using a shunt of and connected as shown in the figure (i). The ammeter reads . The same galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter by connected a resistance of in series. This voltmeter is connected as shown in figure (ii). Its reading is found to be of the full scale reading. Find
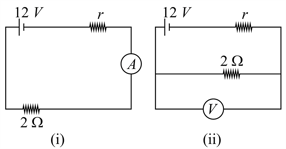
(iii) full scale deflection current of the galvanometer
An accumulator of emf and negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire of length and resistance . The appropriate terminals of a cell of emf and internal resistance is connected to one end of the wire and the other terminal of the cell is connected through a sensitive galvanometer to a slider on the wire. What is the length of the wire that will be required to produce zero deflection of the galvanometer? How will the balancing length change?
(a) When a coil resistance is placed in series with the accumulator.
(b) The cell of is shunted with a resistor?
