MEDIUM
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A glass beaker is filled with water up to . It is kept on top of a thick glass slab. When a coin at the bottom of the glass slab is viewed at the normal incidence from above the beaker, its apparent depth from the water surface is . Value of is close to (the refractive indices of water and glass are and respectively)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
100% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Ray Optics
MEDIUM
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
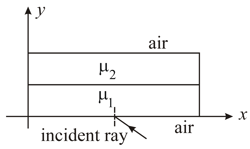
Two thin slabs of refractive indices and are placed parallel to each other in the plane. If the direction of propagation of a ray the two media are along the unit vectors and then we have
EASY
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
For a small air bubble, located below inside a glass sphere (Refractive index) of radius is viewed normally from outside as shown in the figure below. Find the apparent depth (aproximately) of the bubble.
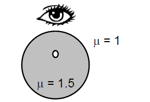
MEDIUM
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
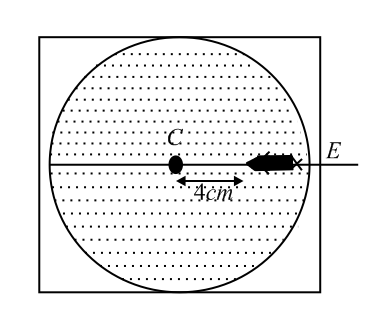
In a thin spherical fish bowl of radius filled with water of refractive index , there is a small fish at a distance of from the centre as shown in the figure. Where will the image of fish appear, if seen from ?
MEDIUM
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
[ Assume both surfaces of the lens have same radius of curvature ]
MEDIUM
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
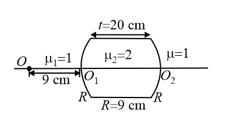
In the given figure, if object is placed at a distance of from , then find the image distance from •
EASY
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
EASY
KCET (UG)
IMPORTANT
