A horizontal straight wire long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of , at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field. a) What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire? (b) What is the direction of emf? c) Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?

Important Questions on Electromagnetic Induction
A rectangular wire loop of sides and with a small cut is stationary but the current feeding the electromagnet that produces the magnetic field is gradually reduced so that the field decreases from its initial value of at the rate of . If the cut is joined and the loop has a resistance of , how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat? What is the source of this power?
Figure below shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutually perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod , , resistance of the closed loop containing the rod . Assume the field to be uniform.

With K open and the rod is moved with a velocity in the direction shown. Give the polarity and magnitude of induced emf.
Figure below shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutually perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod , , resistance of the closed loop containing the rod . Assume the field to be uniform.
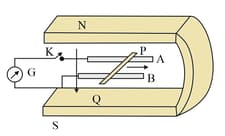
Is there an excess charge built up at the ends of the rod when K is open? What if K is closed?
