A jar is filled with two non-mixing liquids and having densities and respectively. A solid ball, made of a material of density is dropped in the jar. It comes to equilibrium in the position shown in the figure.
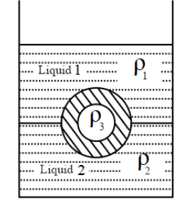
Which of the following is true for and ?


Important Questions on Fluid Mechanics
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of extends above the mercury level. The open-end of the tube is then closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by an additional. What will be length of the air column above mercury in the tube now? (Atmospheric pressure)
A ball of density d is dropped onto a horizontal solid surface. It bounces elastically from the surface and returns to its original position in a time t1. Next, the ball is released and it falls through the same height before striking the surface of a liquid of density
If obtain an expression for the time the ball takes to come back to the position from which it was released.
Is the motion of the ball simple harmonic?
If how does the speed of the ball depend on its depth inside the liquid ?
Neglect all frictional and other dissipative forces. Assume the depth of the liquid to be large.
A container of large uniform cross-sectional area resting on a horizontal surface, holds two immiscible, non-viscous and incompressible liquids of densities and , each of height as shown in the figure. The lower density liquid is open to the atmosphere having pressure .
A homogeneous solid cylinder of length , cross-sectional area is immersed such that it floats with its axis vertical at the liquid-liquid interface with the length in the denser liquid. Determine:
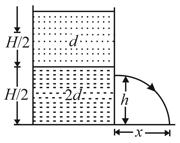
The density of the solid and The total pressure at the bottom of the container.
The cylinder is removed and the original arrangement is restored. A tiny hole in the area is punched on the vertical side of the container at a height , . Determine:
The initial speed of efflux of the liquid at the hole.
The horizontal distance travelled by the liquid initially and
The height hm at which the hole should be punched so that the liquid travels the maximum distance initially. Also, calculate .
