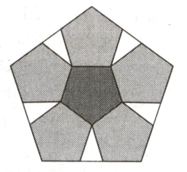
A larger regular pentagon contains smaller pentagons of the same size, as shown in the following diagram. If each side of each of the congruent pentagons is find the total area (in ) covered by the larger pentagon.


Important Questions on Geometry
In the following figure a regular pentagon inscribes a regular pentagram. If each side of the pentagon measures and find the area of pentagram in terms of

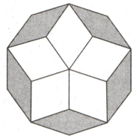
In the following diagram a regular decagon consists of parallelograms, out of which parallelograms that are meeting at the centre are congruent to each other and other parallelograms at the edges of the decagon are congruent to each other. If each side of the decagon is find total area of the parallelograms that are connected to the centre of the decagon.
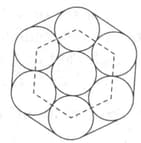
Take seven circles and close-pack them together in a hexagonal arrangement, as shown below. Then a rubber band is wrapped around the seven circles. Find the perimeter of this arrangement, if the radius of each circle is
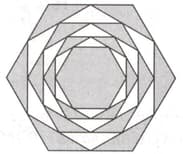
In the given diagram, there are total seven regular hexagons. Let's call the outermost (or the largest) hexagon as and so call the innermost (or the smallest) hexagon as The hexagon is formed by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of Similarly, and are formed by joining the mid-point of the adjacent sides of the and Respectively. If each side of the is Find each side of the
In the given figure there are twelve rhombi placed in such a way that they form a regular hexagram at the centre and this hexagram is inscribed within a regular hexagon. If the area of the hexagon is find the total area of all the twelve rhombi.
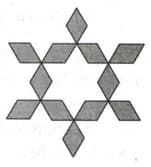
As shown in the given figure, there is a total of seven regular hexagons; six of them are placed around the seventh hexagon. Partially overlapping, and then some rhombi are cut out of the whole arrangement. If the area of the unshaded region represented by the Rhombi is, Find the area of the shaded region.
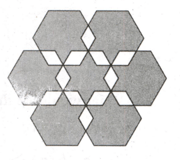
If the area of all the shaded equilateral triangles of the largest possible size, as shown along the periphery of the regular hexagon, is then find the total area of the shaded region of the whole figure.
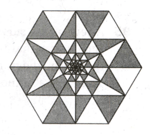
There are seven concentric regular hexagons depicted in the adjacent figure such that they form a six alternating black and white hexagonal rings around a black hexagon. If the area of each hexagonal ring is same and equal to the black hexagon at the centre, find the ratio of the sides of the largest hexagon to that of the smallest hexagon of this arrangement.

