A length of wire carries a steady current. It is bent first to form a circular plane coil of one tum. The same length is now bent more sharply to give a double loop of smaller radius. When the same current is passed, find the ratio of the magnetic field at the centre with its first value.

Important Questions on Magnetic Effect of Current
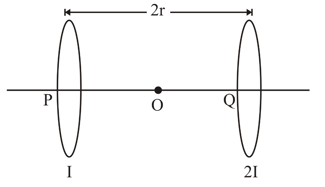
Two identical circular loops, and , each of radius and carrying currents and respectively are lying in parallel planes such that they have a common axis. The direction of current in both the loops is clockwise as seen from which is equidistant from the both loops. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point .
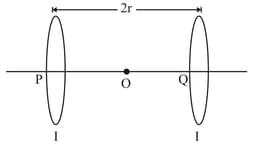
Two identical circular loops, and , each of radius and carrying currents are kept in the parallel planes having a common axis passing through . The dimlion of rurrent in is clockwise and in is anti-clockwise as seen from which is equidistant from the loops and . Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at .
Two small identical circular loops, marked and , carrying equal currents, are placed with the geometrical axes perpendicular to each other as shown in Figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field produced at the point .
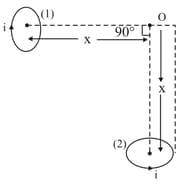
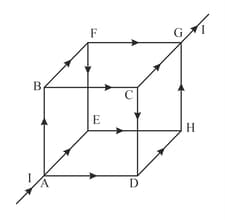
Figure shows a cube made from a uniform wire. Find the magnetic field at the centre of the cube, if a battery is connected between the points and .
(a) a uniform electrostatic field, with initial velocity
(i) parallel to the field,
(a) a uniform electrostatic field, with initial velocity
(i) parallel to the field,
(a) a uniform electrostatic field, with initial velocity
(iii) at an arbitrary angle with the field direction.
