A lens of diameter and focal length was cut along the diameter into two identical halves. In the process, the layer of the lens, in thickness, was lost. Then the halves were put together to form a composite lens. In this focal plane, a narrow slit was placed, emitting monochromatic light with wavelength . Behind the lens a screen was located at a distance from it. Find:
(a) the width of a fringe on the screen and the number of possible maxima;
(b) the maximum width of the slit at which the fringes on the screen will be still observed sufficiently sharp.

Important Questions on OPTICS
A plane light wave with wavelength falls normally on the base of a biprism, made of glass with refracting angle . Behind the biprism there is a plane-parallel plate, with the space between them filled up with benzene . Find the width of a fringe on the screen placed behind this system.
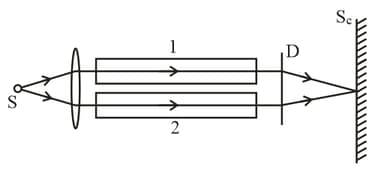
Figure illustrates an interferometer used in measurement of refractive indices of transparent substances. Here is a narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic light with wavelength , and are identical tubes with air of length each, is a diaphragm with two slits. After the air in tube was replaced with ammonia gas, the interference pattern on the screen was displaced upward by fringes. The refractive index of air is equal to . Determine the refractive index of ammonia gas.
An isotropic point source emits light with wavelength . The radiation power of the source is . Find
(a) the mean density of the flow of photons at a distance from the source.
(b) the distance between the source and the point at which the mean concentration of photons is equal to .
Planck's constant and speed of light
