A light ray falling at an angle of with the normal on the surface of a clean slab of ice of thickness is refracted into it at an angle of . Calculate the time taken by the light rays to cross the slab. Speed of light in vacuum.

Important Questions on Ray Optics
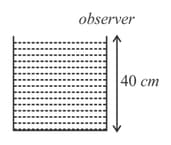
In the given figure, an observer in air sees the bottom of a beaker filled with water upto a height of . What will be the depth felt by this observer.
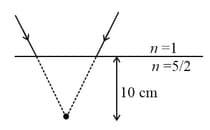
In the given figure, rays incident on an interface would converge below the interface if they continued to move in straight lines without bending. But due to refraction, the rays will bend and meet some where else. Find the distance of meeting point of refracted rays below the interface, assuming that the rays to be making small angles with the normal to the interface.
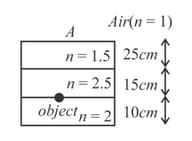
Find the apparent depth of the object seen by observer (in the figure shown)
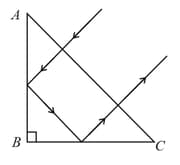
At what values of the refractive index of a rectangular prism can a ray travel as shown in the figure. The section of the prism is an isosceles triangle and the ray is normally incident onto the face .