EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A man can swim certain distance in still water up and down in time . If he swims to some distance down stream the river and returns back to same point he takes time . Then,
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) and cannot be compared
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Kinematics
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A train of length is moving with a speed of in North direction. A small bird is flying above the train with a speed of in south direction. Find the time taken by the bird to cross the train in seconds.
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A boy standing on the foothpath tosses a ball straight up and catches it. The driver of a car passing by moving with uniform velocity sees this.
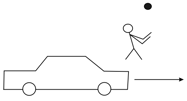
The trajectory of the ball as seen by the driver will be
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A particle of unit mass undergoes one dimensional motion such that its velocity varies according to , where b and n are constants and is the position of the particle. The acceleration of the particle as the function of , is given by:
