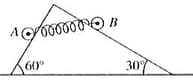
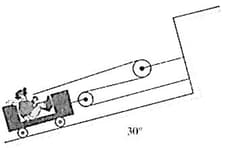
A man pulls himself up the incline by the method shown in figure. If the combined mass of the man and cart is , determine the acceleration of the cart if the man exerts a pull of on the rope. Neglect all friction and the mass of the rope, pulleys, and wheels.


Important Questions on Newton's Laws of Motion (Without Friction)
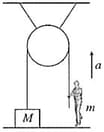
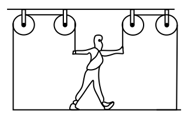
A painter of mass stands on a platform of mass and pulls himself up by two ropes which hang over pulley as shown in the figure. He pulls each rope with force and moves upward with a uniform acceleration . Find , neglecting the fact that no one could do this for long time.
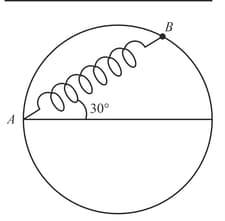
A bead of mass is attached to one end of a spring of natural length and spring constant . The other end of the spring is fixed at a point on a smooth vertical ring of radius as shown in the figure. The normal reaction at just after it is released to move is
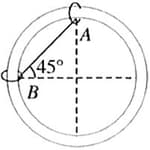
Two objects and , each of mass , are connected by a light inextensible string. They are restricted to move on a frictionless ring of radius in a vertical plane (as shown in figure). The objects are released from rest at the position shown. Then the tension in the cord just after release is
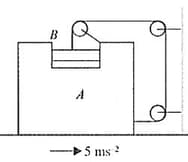
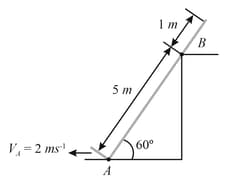
If block is moving with an acceleration of , the acceleration of with respect to ground is,
Two uniform solid cylinders and each of mass are connected by a spring of constant at their axles and are placed on a fixed wedge as shown in the figure. There is no friction between cylinders and wedge. The angle made by the line with the horizontal, in equilibrium, is
The velocity of point on the rod is (leftwards) at the instant shown in the figure. The velocity of the point on the rod at this instant is
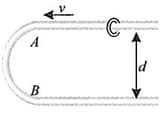
A fixed shaped smooth wire has a semi-circular bending between and as shown in figure. bead of mass moving with uniform speed through the wire enters the semicircular bend at and leaves at . The average force exerted by the bead on the part of the wire is