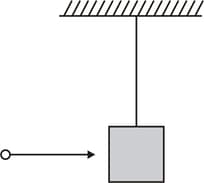
A mass of moving horizontally with a velocity of strikes the bob of a pendulum and sticks to it. The mass of the bob is also . The maximum height to which the system can be raised is

Important Questions on Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions
Assertion: A sphere of mass moving with speed undergoes a perfectly elastic head-on collision with another sphere of heavier mass at rest , then the direction of the velocity of the sphere of mass is reversed due to collision [no external force acts on a system of two spheres]
Reason: During a collision of spheres of unequal masses, the heavier mass exerts more force on lighter mass in comparison to the force which lighter mass exerts on heavier mass.
Assertion: If the mass of the colliding particles remains constant, then the linear velocity of the individual particles change during collision along common normal direction.
Reason: A pair of equal and opposite impulses act along common normal direction.
Assertion : A shell at rest, explodes. The centre of mass of fragments moves along a straight path.
Reason : In explosion the linear momentum of the system remains always conserved.
Reason: Product of mass of one particle and its distance from the centre of mass is numerically equal to the product of the mass of other particle and its distance from the centre of mass.
Reason: Centre of mass of a body is a point, where the whole mass of the body is supposed to be concentrated.
Reason: Centre of mass is same for all bodies.
