EASY
Earn 100
A particle moves along a curve of unknown shape but magnitude of force F is constant and always acts along tangent to the curve. Then
(a) may be conservative
(b) must be conservation
(c) may be non - conservative
(d) must be non - conservative
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
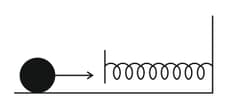
A mass of moving with a speed of on a horizontal smooth surface, collides with a nearly weightless spring of force constant . The maximum compression of the spring would be
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
The graphs below show the magnitude of the force on a particle as it moves along the positive -axis from the origin to . The force is parallel to the -axis and conservative. The maximum magnitude has the same value for all graphs. Rank the situations according to the change in the potential energy associated with the force, least (or most negative) to greatest (or most positive).

MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
EASY

