HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A particle moves such that its position vector , where is a constant and is time. Then which of the following statements is true for the velocity and acceleration of the particle:
(a) is perpendicular to and is directed away from the origin
(b) and both are perpendicular to
(c) and both are parallel to
(d) is perpendicular to and is directed towards the origin
14.29% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Kinematics
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A ball is dropped from the top of a high tower on a planet. In the last before hitting the ground, it covers a distance of Acceleration due to gravity (in ) near the surface on that planet is______
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
The distance covered by a particle in one dimensional motion varies with time as . If the acceleration of the particle depends on as , where is an integer, the value of is _________
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
One end of a straight uniform long bar is pivoted on horizontal table. It is released from rest when it makes an angle from the horizontal (see figure). Its angular speed when it hits the table is given as , where is an integer. The value of is ____________
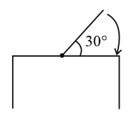
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A particle starts from the origin at with an initial velocity of and moves in the plane with a constant acceleration . The coordinate of the particle at the instant when its coordinate is is meters. The value of is:
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
The stream of a river is flowing with a speed of . A swimmer can swim at a speed of . The direction of the swimmer with respect to the flow of the river, to cross the river straight, is
HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
The position of a particle as a function of time is given by where and are constants. When the particle has zero acceleration, then its velocity will be:
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
The position vector of a particle changes with time according to the relation What is the magnitude of the acceleration at
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A particle is moving with a velocity where is a constant.
The general equation for its path is:
