A plane mirror long, is hung on a vertical wall of a room, with its lower edge above the ground. A man stands in front of the mirror at a distance away from the mirror. If his eyes are at a height above the ground, then the length (distance between the extreme points of the visible region perpendicular to the mirror) of the floor visible to him due to reflection from the mirror is . Find the value of .

Important Questions on Ray Optics
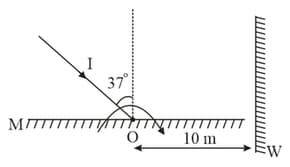
A light ray is an incident on a plane mirror . The mirror is rotated in the direction as shown in the figure by an arrow at frequency . The light reflected by the mirror is received on the wall at a distance from the axis of rotation. When the angle of incidence becomes the speed of the spot (a point) on the wall is . Find the value of .
A convex mirror and a concave mirror each of focal length are placed coaxially. They are separated by and their reflecting surfaces face each other. A point object is kept on the principal axis at a distance from the concave mirror such that the final image after two reflections, first on the concave mirror, is on the object itself. Write the value of to the nearest integer.
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror of radius of curvature at a distance from the pole of the mirror. A glass slab of thickness and refractive index is placed between object and mirror as shown in the figure.
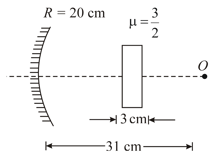
Find the distance of the final image formed by the system from the mirror.
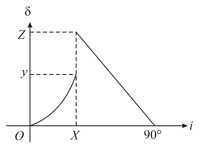
Light is incident from glass to air. The variation of the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence for is shown. The refractive index of glass is . If the value of is , then find the value of .
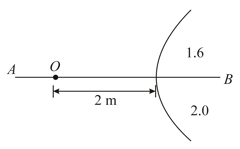
In the figure shown a point object is placed in the air. The spherical boundary of the radius of curvature separates two media. is the principal axis. The refractive index above is and below is . Find the separation between the images formed due to refraction at the spherical surface.
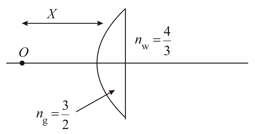
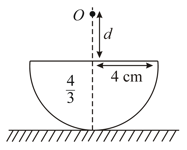
A glass hemisphere of refractive index and of the radius is placed on a plane mirror. A point object is placed on the axis of this sphere at a distance from as shown in the figure. If the final image is formed at infinity, then find the value of
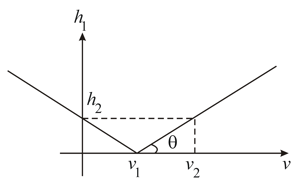
An object of height is moved along the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length . The figure shows the variation of the magnitude of the height of the image with image distance . Find .
In the given figure an object is kept in the air in front of a thin plano-convex lens of the radius of curvature . Its refractive index is and the medium towards the right of the plane surface is the water of refractive index . What should be the distance of the object so that the rays become parallel finally.