A plane mirror produce a magnification of
Important Questions on Reflection and Spherical Mirror
A cylindrical transparent vessel of height , where is the radius of the vessel, is filled with an ideal gas of molar mass at a temperature and a pressure . The dependence of the refractive index of the gas on its density obeys the law . The vessel is rotated at an angular velocity about its axis. A narrow parallel beam of light of radius is incident along the axis of the vessel.
Determine the radius of the spot on the screen placed at right angles to the vessel axis at a distance behind the vessel, assuming that the change in the gas pressure at each point of the vessel due to rotation is small as compared with . The effect of the end faces of the vessel on the path of the rays should be neglected.
The beam from an argon laser (of wavelength ) has a diameter of and a continuous energy output rate of The beam is focused onto a diffuse surface by a lens whose focal length is A diffraction pattern is formed, the radius of the central disk being given by . The central disk can be shown to contain of the incident power. What is the radius of the central disk? What is the average intensity (power per unit area) in the incident beam? What is the average intensity in the central disk?
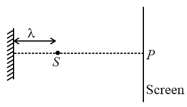
A monochromatic light source , is placed between a mirror and a screen as shown in the figure below,
Remote objects are viewed through a converging lens with a focal length placed at a distance in front of the eye.
Estimate the minimum size of the screen that should be placed behind the lens so that the entire field of view is covered. Where should the screen be placed? Assume that the radius of the pupil is approximately .

