A plano-convex lens of refractive index and focal length is kept in contact with another plano-concave lens of refractive index and focal length . If the radius of curvature of their spherical faces is each and , then and are related as:
Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces : Lenses
A convex lens is put from a light source and it makes a sharp image on a screen, kept from the lens. Now a glass block (refractive index ) of thickness is placed in contact with the light source. To get the sharp image again, the screen is shifted by a distance . Then is:
Formation of real image using a biconvex lens is shown below:
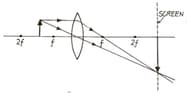
If the whole set-up is immersed in water without disturbing the object and the screen position, what will one observe on the screen?
A plano-convex lens (focal length . refractive index , radius of curvature ) fits exactly into a plano-concave lens (focal length ’ refractive index , radius of curvature ). Their plane surfaces are parallel to each other. Then, the focal length of the combination will be:
An object is at a distance of from a convex lens of focal length . The lens forms an image of the object. If the object moves away from the lens at a speed of , the speed and direction of the image will be:
Two similar thin equi-convex lenses, of focal length each, are kept coaxially in contact with each other such that the focal length of the combination is . When the space between the two lenses is filled with glycerine (which has the same refractive index () as that of glass) then the equivalent focal length is . The ratio will be:
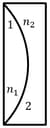
One plano-convex and one plano-concave lens of same radius of curvature ‘’ but of different materials are joined side-by-side as shown in the figure.If the refractive index of the material of is and that of is , then the focal length of the combination is:
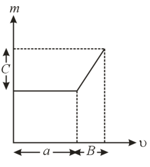
The graph shows how the magnification produced by a thin lens varies with image distance . What is the focal length of the lens used?