A point charge is placed at a distance perpendicular to the plane and above the centre of a square of side . The electric flux through the square is

Important Questions on Electric Charges and Fields
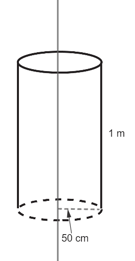
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius . The charge per cm length of the wire is Coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius and length symmetrically encloses the wire as shown in the figure. The total flux passing through the cylindrical surface is
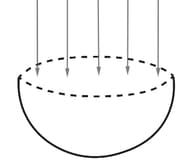
In the figure shown, a hemispherical bowl of radius is shown. Electric field of intensity is present perpendicular to the circular cross section of the hemisphere. The electric flux through the hemisphere is
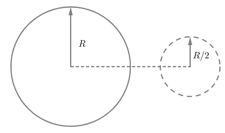
A ring of radius having a linear charge density moves towards a solid imaginary sphere of radius so that the centre of ring passes through the centre of the sphere. The axis of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres of the ring and the sphere. The maximum flux through the sphere in this process is
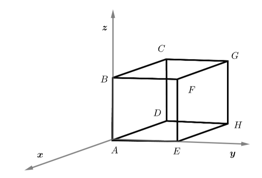
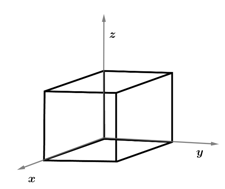
The electric field in a region is given by . Then find the charge enclosed in the cube of side oriented as shown in the diagram.
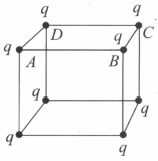
Eight point charges (can be assumed as small uniformly charged spheres and their centres at the corner of the cube) each having values are fixed at vertices of a cube. The electric flux through the square surface of the cube is
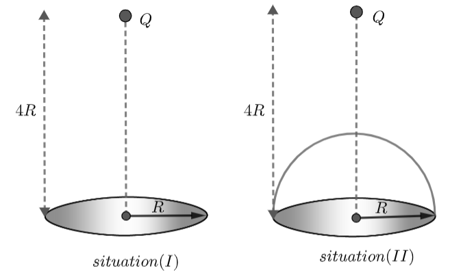
A charge is placed at a distance of above the centre of a disc of radius The magnitude of electric flux through the disc is Now, a hemispherical shell of radius is placed over the disc such that it forms a closed surface. The flux through the curved surface taking the direction of area vector along outward normal as positive is
The figure below shows a closed Gaussian surface in the shape of cube of edge length . There exists an electric field given by where is in metres in the region in which it lies. The net charge (in Coulombs) enclosed by the cube is equal to