A point charge is located at the centre of a spherical layer of uniform isotropic dielectric, with permittivity . The inside radius of the layer is equal to , the outside radius is . Find the electrostatic energy inside the dielectric layer.

Important Questions on ELECTRODYNAMICS
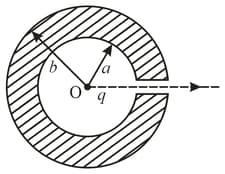
A point charge is located at the centre of a spherical uncharged conducting layer, provided with a small orifice (figure). The inside and outside radii of the layer are equal to and , respectively. What amount of work has to be performed to slowly transfer the charge from the point , through the orifice and into infinity?
Each plate of a parallel-plate air capacitor has an area . What amount of work has to be performed to slowly increase the distance between the plates from to , if
(a) the charge of the capacitor, which is equal to or
(b) the voltage across the capacitor, which is equal to , is kept constant in the process?
Inside a parallel-plate capacitor, there is a plate parallel to the outer plates, whose thickness is equal to of the gap width. When the plate is absent, the capacitor capacitance equals . First, the capacitor was connected in parallel to a constant voltage source, producing , then it was disconnected from it, after which the plate was slowly removed from the gap. Find the work performed during the removal, if the plate is
(a) made of metal;
(b) made of glass.
(Permittivity of vacuum, )
A parallel-plate capacitor is located horizontally, so that one of its plates is submerged into liquid while the other is over its surface (figure). The permittivity of the liquid is equal to , its density is equal to . To what height will the level of the liquid in the capacitor rise after its plates get a charge of surface density ?