A positively charged rod is brought near to a non-conducting object. The rod is attracted to the object. From this observation, we can't predict whether the object is charged or uncharged. Some additional experiments have been performed to identify whether the object is charged or uncharged. These experiments, with their observations and conclusions drawn are given. Select the option in which the conclusion drawn is correct.

Important Questions on Coulomb's Laws and Electric Field
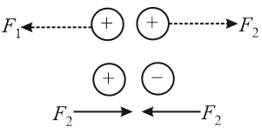
In two cases, two identical conducting spheres are given equal charges, in one case of the same type whereas in another case of the opposite type. The distance between the spheres is not large as compared with the diameter. Let and be the magnitude of the force of interaction between the spheres, as shown, then
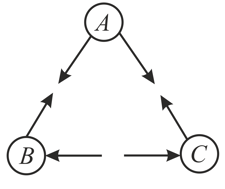
The diagram shows the arrangement of three small uniformly charged spheres , and . The arrows indicate the direction of the electrostatic forces acting between the spheres (for example, the left arrow on sphere indicates the electrostatic force on sphere due to sphere ). At least two of the spheres are positively charged. Which sphere, if any, could be negatively charged?
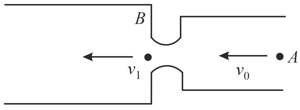
The velocity of an electron at point is , where the cross-sectional area is. The velocity of the electron at the end of contraction at point , where the cross-sectional area is , is . Find the correct option.
Select the correct statement(s) with respect to charges.
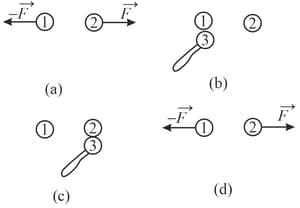
Identical isolated conducting spheres and have equal charges and are separated by a distance that is large compared with their diameters (figure ). The electrostatic force acting on sphere due to sphere is . Suppose that a third identical sphere, having an insulating handle and initially neutral, is touched first to sphere (figure ), then to sphere (figure ), and finally removed (figure ). The electrostatic force that now acts on sphere has magnitude . What is the ratio ?
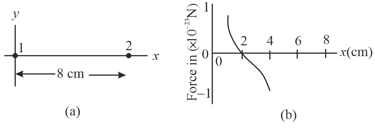
In Figure , particle (of charge ) and particle (of charge ) are fixed in place on -axis, apart. Particle (of charge ) is to be placed on the line between particles and . Figure gives the -component of that force versus the -coordinate at which particle is placed. The scale of the -axis is set by . What is the sign of charge ?