EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A pot with a steel bottom thick, rests on a hot stove. The area of the bottom of the pot is . The water inside the pot is at and are evaporated every . Find the temperature of the lower surface of the pot which is in contact with the stove. Take and .

Important Questions on Calorimetry and Heat Transfer
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A carpenter builds an outer house wall with a layer of wood thick on the outside and a layer of an insulation thick as the inside wall surface. The wood has and the insulation has . The interior surface temperature is and the exterior surface temperature is .
(a) What is the temperature at the plane where the wood meets the insulation?
(b) What is the rate of heat flow per square metre through this wall?
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A closed thermally insulated vessel contains of water at . If air from this vessel is rapidly pumped out, intensive evaporation will produce cooling and as a result of this, water freezes. How much ice will be formed by this method, if latent heat of fusion is and of evaporation ?
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
In a container of negligible mass, of ice, initially at , is added to of water that has a temperature of . If no heat is lost to the surroundings, what is the final temperature of the system and masses of water and ice in the mixture?
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A certain amount of ice is supplied heat at a constant rate for . For the first , the temperature rises uniformly with time. Then, it remains constant for the next , and again the temperature rises at uniform rate for the last . Calculate the final temperature at the end of . (Given: of ice and specific heat of water )
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
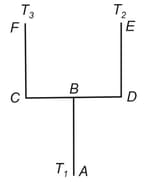
Four identical rods and are joined, as shown in the figure. The length, cross-sectional area and thermal conductivity of each rod are and , respectively. The ends and are maintained at temperatures and , respectively. Assuming no loss of heat to the atmosphere, find the temperature at , the mid-point of .
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
The ends of a copper rod of length and area of cross-section , are maintained at and . At the centre of the rod there is a source of heat of power . Calculate the temperature gradient in the two halves of the rod in steady state. Thermal conductivity of copper is .
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A cylindrical rod with one end in a steam chamber and the other end in ice, results in melting of of ice per second. If the rod is replaced by another, with half the length and double the radius of the first, and if the thermal conductivity of the material of the second rod is that of the first, the rate at which ice melts, in , will be
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
Two sheets of thickness and are touching each other. The temperature just outside the thinner sheet is and on the side of the thicker sheet is . The interface temperature and are in arithmetic progression. The ratio of thermal conductivity of the thinner sheet to the thicker sheet is