A proton beam passes without deviation through a region of space where there are uniform transverse mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic field with and . Then the beam strikes a grounded target. Find the force imparted by the beam on the target if the beam current is equal to .

Important Questions on Magnetic Effect of Current
Three infinitely long conductors and are lying in a horizontal plane as shown in the figure. The currents in the respective conductors are . Find the amplitude of the vertical component of the magnetic field at a point , distance '' away from the central conductor .
A square cardboard of side and mass is suspended from a horizontal axis as shown in figure. A single wire is wound along the periphery of board and carrying a clockwise current . At , a vertical downward magnetic field of induction is switched on. Find the minimum value of so that the board will be able to rotate up to horizontal level.
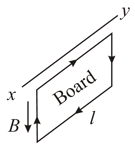
A -shaped wire of mass and length is immersed with its two ends in memory (see figure). The wire is in a homogeneous field of magnetic induction . If a charge, that is, a current pulse , is sent through the wire, the wire will jump up. Calculate, from the height that the wire reaches, the size of the charge or current pulse, assuming that the time of the current pulse is very small in comparison with the time of flight, Make use of the fact that impulse of force equals .
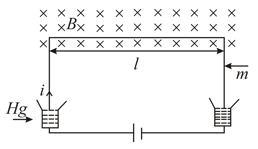
Evaluate for & .
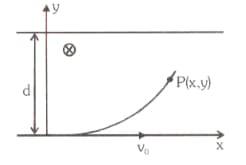
A non-uniform magnetic field is present in region of space in between and . The lines are shown in the diagram. A particle of mass '' and positive charge '' is moving. Given an initial velocity . Find the component of velocity of the particle when leaves the field.
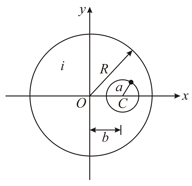
A very long straight conductor has a circular cross-section of radius and carries a current density . Inside the conductor there is a cylindrical hole of radius a whose axis is parallel to the axis of the conductor and a distance from it. Let the -axis be the axis of the conductor, and let axis of the hole be at . Find the magnetic field (i) on the -axis at (ii) on the -axis at