A rectangular loop PQMN with movable arms PQ of length and resistance is placed in a uniform magnetic field of acting perpendicular to the plane of the loop as is shown in the figure.
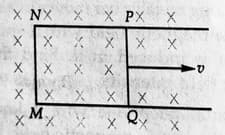
The resistance of the arm MN, NP and MQ are negligible. Calculate the EMF induced in the arm PQ and the current induced in the loop when arm PQ is moved with velocity .

Important Questions on Electromagnetism
What do you mean by electromagnetic induction? Name the two great experimentalists who carried long series of experiments on electromagnetic induction. You are given two coils one galvanometer, one battery and some connecting wires. Describe a experiment that can show the production of electromagnetic induction.
A magnet kept at the centre of two coils and is moved to and fro as shown in the diagram. The two galvanometers show deflection.
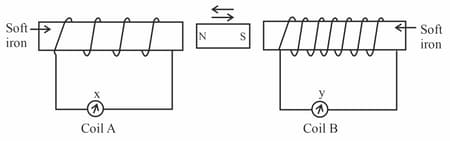
State with a reason whether: or [ and are magnitudes of deflection]
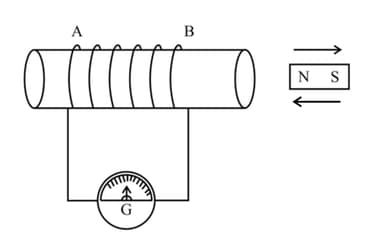
Observe the given diagram. Explain the experiment related to this diagram. What conclusions can be drawn from this experiment?
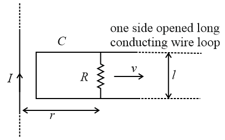
An infinitely long straight wire carrying current , one side opened rectangular loop and a conductor with a sliding connector are located in the same plane, as shown in the figure. The connector has length and resistance . It slides to the right with a velocity . The resistance of the conductor and the self-inductance of the loop are negligible. The induced current in the loop, as a function of separation , between the connector and the straight wire is:
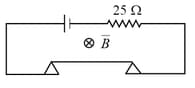
A long thin metal bar of negligible resistance weighing rests on two metal supports as shown in the figure. The supports are connected in series to an ideal cell and a resistance. A uniform magnetic field is applied in the region normal to the plane of the paper and into the paper. Maximum emf that the cell can have without breaking the circuit in volt is
(Acceleration due to gravity )
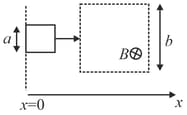
A square-shaped conducting wire loop of dimension a moving parallel to the -axis approaches a square region of size where a uniform magnetic field exists pointing into the plane of the paper (see figure). As the loop passes through this region, the plot correctly depicting its speed as a function of is.
What is electromagnetic induction? A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen in the galvanometer if a bar magnet is (a) pushed into the coil, (b) withdrawn from inside the coil, (c) held stationary inside the coil.

An emf in the coil will be generated for the following situations.
Then, the