A red giant is a star bigger than our Sun. Explain how the surface of a red giant star can be cooler than the Sun, yet have a luminosity much greater than the Sun.

Important Questions on Astronomy and Cosmology
The surface temperature of a star depends on the wavelength at the peak intensity of the emitted radiation from the star. The against graph for a cluster of stars in our galaxy is shown.
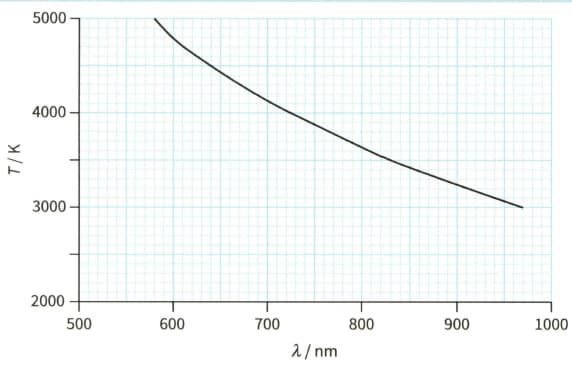
Use the graph to show Wien's displacement law is obeyed.
The surface temperature of a star depends on the wavelength at the peak intensity of the emitted radiation from the star. The against graph for a cluster of stars in our galaxy is shown.
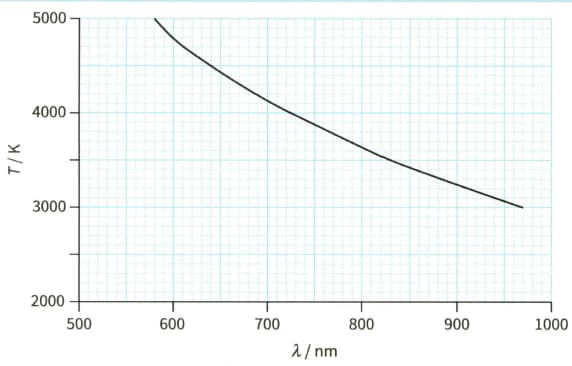
(ii) Estimate the surface temperature of a star with . In your answer, include the absolute uncertainty.
Light from a galaxy is passed through a diffraction grating. The diagram shows part of the emission spectrum.
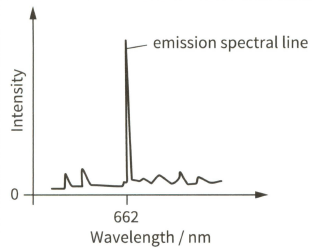
The strong emission spectral line has wavelength .
Calculate the energy of a photon of wavelength .
Light from a galaxy is passed through a diffraction grating. The diagram shows part of the emission spectrum.
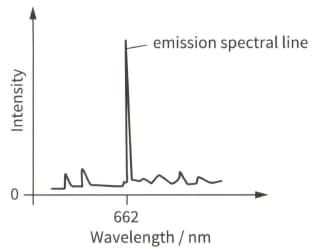
The strong emission spectral line has wavelength 662 nm.
Explain how a spectral line is produced by electrons within atoms.
Light from a galaxy is passed through a diffraction grating. The diagram shows part of the emission spectrum.
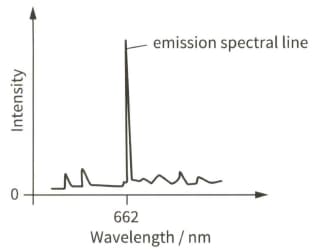
The strong emission spectral line has wavelength 662 nm.
In the laboratory, the same spectral line has wavelength 656 nm.
(i) Calculate the speed of the galaxy.
Light from a galaxy is passed through a diffraction grating. The diagram shows part of the emission spectrum.
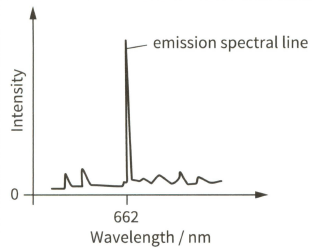
The strong emission spectral line has wavelength 662 nm.
(c) In the laboratory, the same spectral line has wavelength 656 nm.
(ii) State the direction of travel of the galaxy.
Light from a galaxy is passed through a diffraction grating. The diagram shows part of the emission spectrum.

The strong emission spectral line has wavelength 662 nm.
State and explain what the wavelength of the same spectral line would be for a much more distant galaxy.
