A rod has length at a temperature of . Find the free expansion of the rod, if the temperature is increased to , then find stress produced when the rod is permitted to expand by .

Important Questions on Thermometry, Thermal Expansion and Calorimetry
Two rods of different metals having the same area of cross section are placed between the two massive walls as shown in the given figure. The first rod has a length , coefficient of linear expansion and Young's modulus . The corresponding quantities for second rod are and . The temperature of both the rods is now raised by .
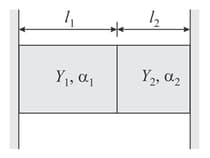
(a) Find the force with which the rods act on each other (at higher temperature) in terms of given quantities.
(b) Also find the length of the rods at higher temperature.
A steel ball initially at a pressure is heated from to keeping its volume constant. Find the pressure inside the ball.
The coefficient of linear expansion of steel is .
Bulk modulus of steel is .
A composite rod is made by joining a copper rod, end to end, with a second rod of different material but of the same area of cross section. At , the composite rod is long and the copper rod is long. At the length of the composite rod increases by . When the composite rod is prevented from expanding by holding it between two rigid walls, it is found that the constituent rods have remained unchanged in length in spite of rise of temperature. Find Young's modulus and the coefficient of linear expansion of the second rod ( of copper and of copper ).
At room temperature the length of a steel rod is measured using a brass centimetre scale. The measured length is . If the scale is calibrated to read accurately at temperature , find the actual length of steel rod at room temperature.
A steel tape long is correctly calibrated for a temperature of . The length of a steel rod measured by this tape is found to be on a hot day when the temperature is . What is the actual length of the steel rod on that day? What is the length of the same steel rod on a day when the temperature is ? Coefficient of linear expansion of steel .
A steel scale measures the length of a copper rod as when both are at , which is the calibration temperature for the scale. What would the scale read for the length of the rod when both are at ? for steel and for copper .
A flask contains some mercury. It is found that at different temperatures, the volume of air inside the flask remains the same. What is the volume of mercury in the flask, given that the coefficient of linear expansion of glass and the coefficient of volume expansion of ?
A glass bottle is completely filled with water at . The bottle and water are heated to . How much water runs over if the expansion of the bottle is neglected.
the expansion of the bottle is neglected;
