A rod of length and cross-section area lies along the -axis between and . The material obeys Ohm's law and its resistivity varies along the rod according to . The end of the rod at is at a potential and it is zero at . (i) Find the total resistance of the rod and the current in the wire (ii) Find the electric potential in the rod as a function of .

Important Questions on Current Electricity
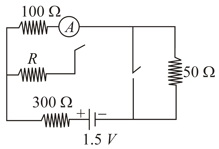
In the circuit shown in figure the reading of ammeter is the same with both switches open as with both closed. Then find the resistance . (ammeter is ideal).
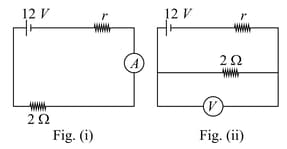
A galvanometer (coil resistance ) is converted into a ammeter using a shunt of and connected as shown in the figure (i). The ammeter reads . The same galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter by connected a resistance of in series. This voltmeter is connected as shown in figure (ii). Its reading is found to be of the full scale reading. Find range of the ammeter and voltmeter.
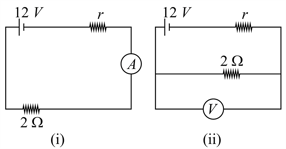
A galvanometer (coil resistance ) is converted into a ammeter using a shunt of and connected as shown in the figure (i). The ammeter reads . The same galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter by connected a resistance of in series. This voltmeter is connected as shown in figure (ii). Its reading is found to be of the full scale reading. Find
(iii) full scale deflection current of the galvanometer
An accumulator of emf and negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire of length and resistance . The appropriate terminals of a cell of emf and internal resistance is connected to one end of the wire and the other terminal of the cell is connected through a sensitive galvanometer to a slider on the wire. What is the length of the wire that will be required to produce zero deflection of the galvanometer? How will the balancing length change?
(a) When a coil resistance is placed in series with the accumulator.
(b) The cell of is shunted with a resistor?
