A sample of ideal gas is heated at constant pressure. If an amount of heat is supplied to the gas, find
(a) the change in internal energy of the gas and
(b) the work done by the gas.

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
curve of a diatomic gas is shown in the figure. Find the total heat given to the gas in the process .
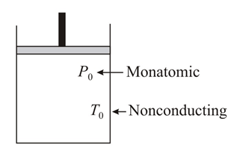
A monatomic gas is enclosed in a nonconducting cylinder having a piston which can move freely. Suddenly gas is compressed to of its initial volume. Find the final pressure and temperature if initial pressure and temperature are and respectively.
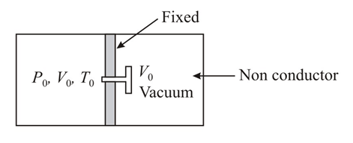
A non-conducting cylinder having volume is partitioned by a fixed non-conducting wall in two equal parts. Partition is attached with a valve. The right side of the partition is a vacuum and the left part is filled with a gas having pressure and temperature and respectively. If the valve is opened find the final pressure and temperature of the two parts.
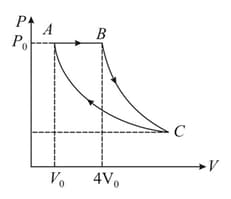
A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process as shown in the figure. It absorbs of heat during the part , no heat during and rejects of heat during . If of work is done on the gas during the part .
(a) Find the internal energy of the gas at and if it is at .
(b) Calculate the work done by the gas during the part
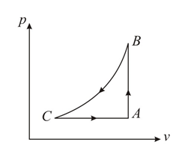
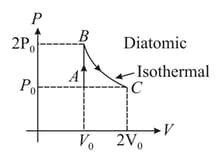
In a cycle consisting of isothermal expansion , isobaric compression and adiabatic compression , find the efficiency of cycle (Given: )
A container of volume is divided into two equal compartment by a partition. One of these compartments contains an ideal gas at . The other compartment is vacuum. The whole system is thermally isolated from its surroundings. The partition is removed and the gas expands to occupy the whole volume of the container. Find the new temperature.
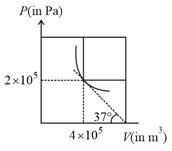
A fixed mass of a gas is taken through a process (as shown in the figure). Here is isobaric, is adiabatic and is isothermal. Find efficiency of the process (take ).