A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass , as shown in the diagram.
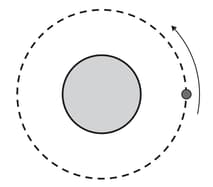
On a copy of the diagram draw arrows to represent the velocity and acceleration of the satellite.


Important Questions on Circular Motion and Gravitation
A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass , as shown in the diagram.
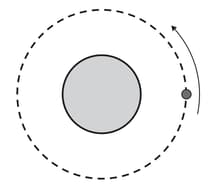
Explain why the satellite has acceleration even though its speed is constant.
A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass , as shown in the diagram.
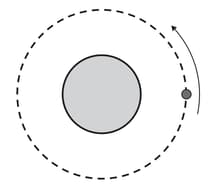
Show that the angular speed is related to the orbit radius by .
A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass , as shown in the diagram.
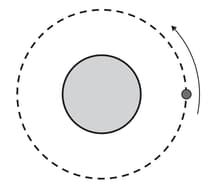
Because of friction with the upper atmosphere, the satellite slowly moves into another circular orbit with a smaller radius than the answer in that is . Suggest the effect of this on the satellite’s:
angular speed
A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass , as shown in the diagram.
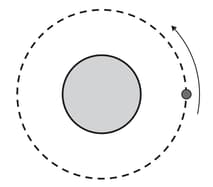
Because of friction with the upper atmosphere, the satellite slowly moves into another circular orbit with a smaller radius than the answer in that is . Suggest the effect of this on the satellite’s:
linear speed.
A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass , as shown in the diagram.
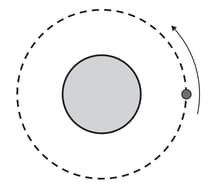
Titan and Enceladus are two of Saturn’s moons. Data about these moons are given in the table.
| Moon | Orbit radius / | Angular speed / |
|---|---|---|
| Titan | ||
| Enceladus |
Determine the mass of Saturn.
A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass , as shown in the diagram.
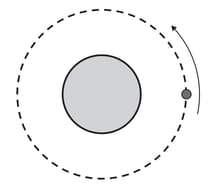
Titan and Enceladus are two of Saturn’s moons. Data about these moons are given in the table.
| Moon | Orbit radius / | Angular speed / |
|---|---|---|
| Titan | ||
| Enceladus |
Determine the period of revolution of Titan in days.
