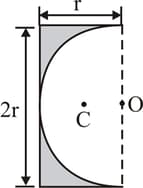
A semicircular portion of radius is cut from a uniform rectangular plate as shown in the figure. The distance of centre of mass of remaining plate from point is:


Important Questions on Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions
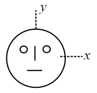
Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink of uniform line-thickness. The mass of ink used to draw each of the two inner circles and each of the two line segments is . The mass of the ink used to draw the outer circle is . The coordinates of the centres of the different parts are: outer circle ; left inner circle , right inner circle , vertical line and horizontal line . The -coordinate of the centre of mass of the ink in this drawing is
A radioactive nucleus initially at rest decays by emitting an electron and neutrino at right angles to one another. The momentum of the electron is and that of the neutrino is . The direction of the recoiling nucleus with that of the electron motion is,
.
A mass moves with a velocity and collides inelastically with another identical mass at rest. After collision, the mass moves with velocity in a direction perpendicular to the initial direction of motion. Find the speed of the mass after collision:
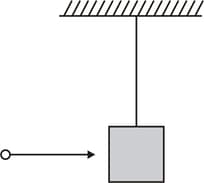
A mass of moving horizontally with a velocity of strikes the bob of a pendulum and sticks to it. The mass of the bob is also . The maximum height to which the system can be raised is
Assertion: A sphere of mass moving with speed undergoes a perfectly elastic head-on collision with another sphere of heavier mass at rest , then the direction of the velocity of the sphere of mass is reversed due to collision [no external force acts on a system of two spheres]
Reason: During a collision of spheres of unequal masses, the heavier mass exerts more force on lighter mass in comparison to the force which lighter mass exerts on heavier mass.
