A simple pendulum is vibrating with an angular amplitude of as shown in the given figure. For what value of is the acceleration directed?
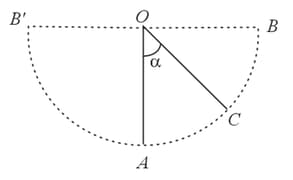
(i) vertically upwards
(ii) horizontally
(iii) vertically downwards


Important Questions on Circular Motion
A car moving at a speed of is taking a turn on a circular road of radius . A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (figure). A small block of mass is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. The friction coefficient between the block and the plate is, .
(a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block.
(b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
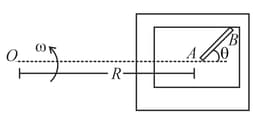
A table with the smooth horizontal surface is fixed in a cabin that rotates with a uniform angular velocity in a circular path of radius (figure). A smooth groove of length is made on the surface of the table. The groove makes an angle with the radius of the circle in which the cabin rotates. A small particle is kept at the point in the groove and is released to move along . Find the time taken by the particle to reach the point .
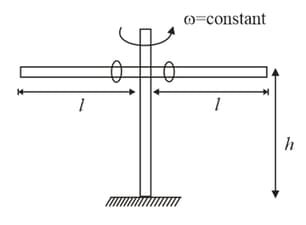
A smooth rod is rotated in a horizontal plane about its mid-point with height, vertically below a fixed point at a constant angular velocity . A light elastic string of natural length requiring has one end fixed at and its other end attached to a ring of mass which is free to slide along the rod. When the ring is stationary relative to the rod, then find inclination of string with vertical, tension in string and force exerted by the ring on the rod .
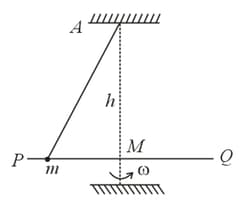
A mass lies on fixed smooth cylinder. An ideal cord attached to passes over the cylinder and is connected to mass as shown in the figure.
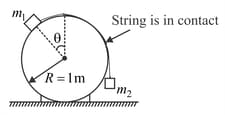
Find the value of in degree (shown in the diagram) for which the system is in equilibrium if and .
A mass lies on fixed smooth cylinder. An ideal cord attached to passes over the cylinder and is connected to mass as shown in the figure.

if . The system is released from rest when . Find the value of if the magnitude of the acceleration of mass just after the system is released is .
Two identical rings which can slide along the rod are kept near the midpoint of a smooth rod of length The rod is rotated with constant angular velocity about the vertical axis passing through its center. The rod is at height from the ground. Find the distance (in meter) between the points on the ground where the rings will fall after leaving the rods.