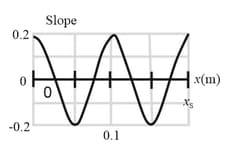
A sinusoidal wave travels along a string under tension. The figure shown below gives the slopes along the string at time The scale of the axis is set by What is the amplitude of the wave?


Important Questions on Waves-I
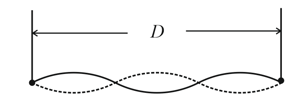
A nylon guitar string has a linear density of and is under a tension of . The fixed supports are distance apart. The string is oscillating in the standing wave pattern shown in the figure shown below. Calculate the (a) speed, (b) wavelength, and (c) frequency of the traveling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave.
A generator at one end of a very long string creates a wave given by
and a generator at the other end creates the wave
Calculate the (a) frequency, (b) wavelength, and (c) speed of each wave. For , what is the location of the node having the (d) smallest, (e) second smallest, and (f) third smallest value of ? For what is the location of the antinode having the (g) smallest.
(h) second smallest, and (i) third smallest value of ?
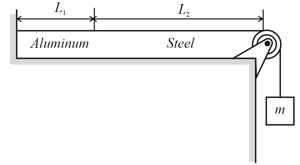
In figure shown below, an aluminum wire, of length cross-sectional area and density is joined to a
steel wire, of density and the same cross-sectional area. The compound wire, loaded with a block of mass is arranged so that the distance from the joint to the supporting pulley is . Transverse waves are set up on the wire by an external source of variable frequency; a node is located at the pulley. (a) Find the lowest frequency that generates a standing wave having the joint as one of the nodes. (b) How many nodes are observed at this frequency?
A string oscillates according to the equation,
What is the
amplitude
speed of the two waves (identical except the direction of travel) whose superposition gives this oscillation?
What is the distance between nodes?
What is the transverse speed of a particle of the string at the position when ?
