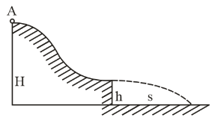
A small disc slides down with initial velocity equal to zero from the top of a smooth hill of height having a horizontal portion. What must be the height of the horizontal portion to ensure the maximum distance covered by the disc? What is it equal to?


Important Questions on PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
A small body starts sliding from the height down an inclined groove passing into a half-circle of radius .
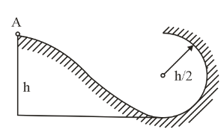
Assuming the friction to be negligible, find the velocity of the body at the highest point of its trajectory (after breaking off the groove).
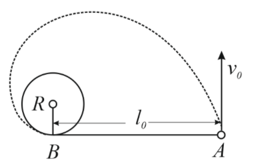
A horizontal plane supports a stationary vertical cylinder of radius and a disc attached to the cylinder by a horizontal thread of length ( top view). An initial velocity , is imparted to the disc as shown in the figure. How long will it move along the plane until it strikes against the cylinder? The friction is assumed to be absent.
A smooth rubber cord of length , whose coefficient of elasticity is , is suspended by one end from the point . The other end is fitted with a catch . A small sleeve of mass starts falling from the point . Neglecting the masses of the thread and the catch, find the maximum elongation of the cord.
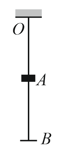
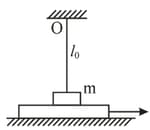
A small bar resting on a smooth horizontal plane is attached by threads to a point , and by means of a weightless pulley, to a weight possessing the same mass as the bar itself.
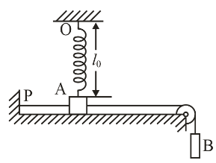
Besides, the bar is also attached to a point by means of a light non-deformed spring of length , and stiffness , where is the mass of the bar. The thread having been burnt, the bar starts moving. Find its velocity at the moment when it is breaking off the plane.
A horizontal plane supports a plank with a bar of mass placed on it and attached by a light elastic non-deformed cord of length to a point . The coefficient of friction between the bar and the plank equals . The plank is slowly shifted to the right until the bar starts sliding over it. It occurs at the moment when the cord deviates from the vertical by an angle . Find the work that has been performed by that moment by the friction force acting on the bar in the reference frame fixed to the plane.