MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A small sphere falls from rest in a viscous liquid. Due to friction, heat is produced. Find the relation between the rate of production of heat and the radius of the sphere at terminal velocity.

Important Questions on Viscosity and Surface Tension
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
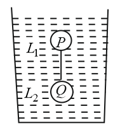
Two spheres and of equal radii have densities and , respectively. The spheres are connected by a massless string and placed in liquids and of densities and viscosities and , respectively. They float in equilibrium with the sphere in and sphere in and the string is being taut (see figure). If sphere alone in has terminal velocity and alone in has terminal velocity , then
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Consider a thin square plate floating on a viscous liquid in a large tank. The height of the liquid in the tank is much less than the width of the tank. The floating plate is pulled horizontally with a constant velocity . Which of the following statements is (are) true?
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Spherical balls of radius Are falling in a viscous fluid of viscosity with a velocity . The retarding viscous force acting on the spherical ball is:
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
A spherical solid ball of volume is made of a material of density . It is falling through a liquid of density . [Assume that the liquid applies a viscous force on the ball that is proportional to the square of its speed , i.e. ]. The terminal speed of the ball is
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge is balanced in still air with a vertical uniform electric field of strength . When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity Given viscosity of the air and the density of oil the magnitude of is:
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Eight raindrops of radius one each falling down with a terminal velocity of coalesces to form a bigger drop. Calculate the terminal velocity of the bigger drop.
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
A long cylinder of the radius is displaced along its axis with a constant velocity , inside a stationary co-axial cylinder of radius . The space between the cylinders is filled with viscous liquid. Find the velocity of the liquid as a function of the distance from the axis of the cylinders. The flow is laminar.
