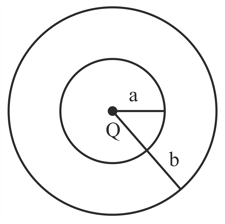
A solid conducting sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be V. If the shell is now given a charge of –3Q, the new potential difference between the same two surfaces is
Important Questions on Electrostatics
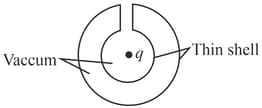
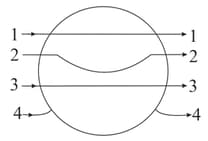
Which one of the following figures correctly indicates the induced charge distribution in the conductor (ignore edge effects).
Two long concentric hollow metallic cylinders of radiiand, respectively carry equal and opposite charges and per unit length, as shown. The space between the cylinders is filled with air. The distance measured from the central axis is denoted by
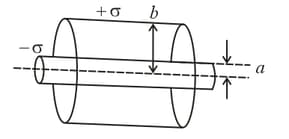 .
.
Which of the following statements is NOT CORRECT?
Given below are two statements.
Statement I : Electric potential is constant within and at the surface of each conductor.
Statement II : Electric field just outside a charged conductor is perpendicular to the surface of the conductor at every point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options give below.
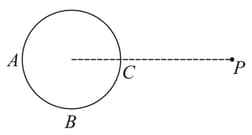
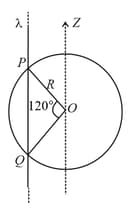
A hollow conducting sphere is placed in an electric field produced by a point charge placed at as shown in figure. Let be the potentials at points and , respectively. Then
Write any five application of superconductors.
for
for .
does not depend on x and y. If this potential is generated by a constant charge per unit volume (in units of ) which is spread over a certain region, then choose the correct statement.
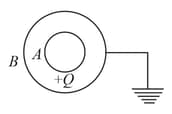
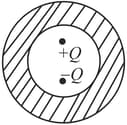
A spherical conductor is placed concentrically inside a hollow spherical conductor . The charge is given to and is earthed. Then the electric field is not zero
Conventionally which coloured wire is used for earthing?
Three concentric spherical shells are arranged as shown in the figure. The innermost and outermost spheres are connected to earth. If the middle sphere is given a charge . the charges induced in the innermost and outermost spheres respectively are
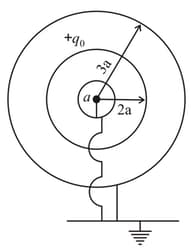
Consider an initially neutral hollow conducting spherical shell with inner radius and outer radius A point charge is now placed inside the shell at a distance from the center. The shell is then grounded by connecting the outer surface to the earth. P is an external point at a distance from the point charge on the line passing through the center and the point charge as shown in the figure.
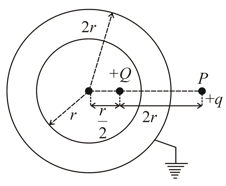
The magnitude of the force on a test charge placed at P will be

