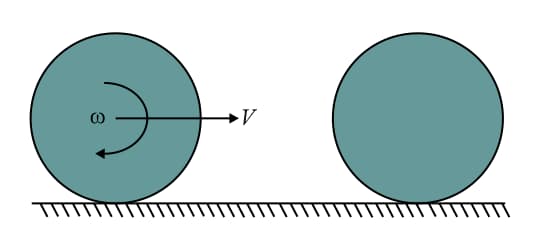
A solid sphere is rolling without slipping on a rough ground as shown in figure. It collides elastically with an identical another sphere at rest. There is no friction between the two spheres. Radius of each sphere is and mass is . The linear velocity of first sphere after it again starts rolling without slipping is,


Important Questions on Rotational Motion
Two masses are moving perpendicular to the rod of mass with velocities as shown in the figure. The length of the rod is . Find the ratio of the final velocity of the rod and its angular velocity if the masses stop at their place after collision.
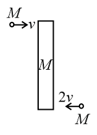
A uniform smooth rod (mass and length ) placed on a smooth horizontal floor is hit by a particle (mass ) moving on the floor, at a distance from one end elastically (). The distance travelled by the centre of the rod after the collision, when it has completed three revolutions, will be
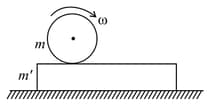
A uniform solid cylinder is given an angular speed and placed on a rough plate of negligible thickness. The horizontal surface below the plate is smooth. Then the angular speed of the cylinder when it starts pure rolling on the plate will be: [Assume sufficient length of plate]
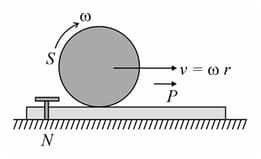
A sphere rolls without slipping, moving with a constant speed on a plank . The friction between the upper surface of and the sphere is sufficient to prevent slipping, while the lower surface of is smooth and rests on the ground. Initially, is fixed to the ground by a pin . If is suddenly removed,
For next 2 question please follow the same
A disc of mass m and radius R is placed over a plank of same mass m. There is sufficient friction between disc and plank to prevent slipping. A force F is applied at the centre of the disc.
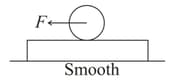
Acceleration of the plank is
