EASY
Earn 100
A space craft of mass M and moving with velocity v suddenly breaks in two pieces of same mass m. After the explosion one of the mass m becomes stationary. What is the velocity of the other part of craft?
(a)
(b)V
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion
EASY
The bodies of mass gram and grams having same kinetics energy having their ratio of linear momentum as
EASY
A bullet of mass is fired from a rifle of mass and the total kinetic energy produced by the explosion is . Then the kinetic energy of the bullet and the rifle are
EASY
An object of mass and travelling at crashes into another object of mass and travelling at in the same direction. After the collision, object bounces back in opposite direction at a speed of . The speed of the object after the collision is
HARD
A particle of mass is projected from the ground with an initial speed at an angle with the horizontal. At the highest point of its trajectory, it makes a completely inelastic collision with another identical particle, which was thrown vertically upward from the ground with the same initial speed . The angle that the composite system makes with the horizontal immediately after the collision is
EASY
Two particles of masses and have equal kinetic energies. The ratio of their momentum is:
EASY
A bomb at rest explodes into parts of same mass. The momentum of two parts is and respectively. The magnitude of momentum of the third part is
EASY
The kinetic energy of a body is increased by . Its momentum increases by
MEDIUM
A block of mass m attached to a massless spring is performing oscillatory motion of amplitude 'A' on a frictionless horizontal plane. If half of the mass of the block breaks off when it is passing through its equilibrium point, the amplitude of oscillation for the remaining system become ƒA. The value of ƒ is:
EASY
If momentum is decreased by , kinetic energy will decrease by
EASY
An object of mass collides with another object of mass , which is at rest. After the collision the objects move with equal speeds in opposite direction. The ratio of the masses is :
EASY
Two particles of masses move with initial velocities and . On collision, one of the particles get excited to higher level, after absorbing energy If final velocities of particles be and then we must have:
EASY
Two masses of and are moving with equal kinetic energy. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momentum is
MEDIUM
A ball is thrown vertically up (taken as ) from the ground. The correct momentum-height diagram is:
EASY
A shell of mass is at rest initially. It explodes into three fragments having mass in the ratio . If the fragments having equal mass fly off along mutually perpendicular directions with speed , the speed of the third (lighter) fragment is:
HARD
A man (mass ) and his son (mass ) are standing on a frictionless surface facing each other. The man pushes his son so that he starts moving at a speed of with respect to the man. The speed of the man with respect to the surface is:
MEDIUM
Given the masses of various atomic particles , , , , , where proton, neutron, electron, antineutrino and deuteron. Which of the following process is allowed by momentum and energy conservation :
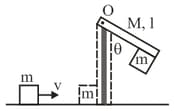
MEDIUM
A block of mass slides with velocity on a frictionless horizontal surface and collides with a uniform vertical rod and sticks to it as shown. The rod is pivoted about and swings as a result of the collision making angle before momentarily coming to rest. if the rod has mass and length the value of is approximately
EASY
The momentum of a body increases by , its kinetic energy increases by (assume that mass does not change)
EASY
Two bodies of mass and have equal kinetic energy. What is the ratio of their momentum?
EASY
Two particles which are initially at rest move towards each other under the action of their mutual attraction. If their speeds are and at any instant, then the speed of center of mass of the system is,

