MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A spotlight rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity of . The spot of the light, moves along the wall at a distance . What is the velocity of the spot when ?
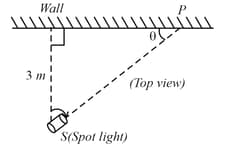

(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Circular Motion
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
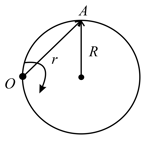
A particle moves along a circle of radius, so that its radius vector , relative to the point (figure), rotates with the constant angular velocity, . Then, the modulus of the velocity of the particle and the modulus of its total acceleration will be,
HARD
NEET
IMPORTANT
A particle of mass moves along a circle of radius with a normal acceleration varying with time as, , where is a constant. Find the time dependence of the power , developed by all the forces acting on the particle, and the mean value of this power averaged over a time after the beginning of the motion.
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
A string breaks if its tension exceeds . A stone of mass , tied to this string of length , is rotated in a horizontal circle. The maximum angular velocity of rotation can be,
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
A particle moves in a circular orbit under the action of a central attractive force inversely proportional to the distance . The speed of the particle is,
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
A particle of mass is moving in a horizontal circle of radius under a centripetal force equal to . The total kinetic energy of the particle is,
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
A stone is projected with speed and angle of projection is . Find the radius of curvature at .
HARD
NEET
IMPORTANT
The velocity and acceleration vectors of a particle undergoing circular motion are and , respectively, at an instant of time. The radius of the circle is,
HARD
NEET
IMPORTANT
A particle is projected horizontally from the top of a tower with a velocity . If is its velocity at any instant, then the radius of curvature of the path of the particle at that instant is directly proportional to,
