A spring and block are in the arrangement as in the figure shown below. When the block is pulled out to , we must apply a force of magnitude to hold it there. We pull the block to and then release it. How much work does the spring do on the block as the block moves from to (a) , (b) , (c) , and (d) ?

Important Questions on Kinetic Energy and Work
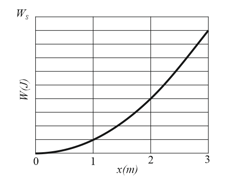
In the arrangement of in the figure shown below we gradually pull the block from to , where it is stationary. The figure shown below gives the work that our force does on the block. The scale of the figure's vertical axis is set by . We then pull the block out to and release it from rest. How much work does the spring do on the block when the block moves from to (a) , (b) and (c) ?
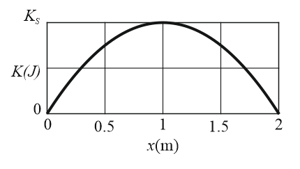
In the figure shown below a block of mass lies on a horizontal frictionless surface and is attached to one end of a horizontal spring (spring constant ) whose other end is fixed. The block is initially at rest at the position where the spring is unstretched when a constant horizontal force in the positive direction of the -axis is applied to it. A plot of the resulting kinetic energy of the block versus its position is shown in the figure shown below. The scale of the vertical axis is set by (a) What is the magnitude of ? (b) What is the value of ?
As a body moves in the positive direction along an -axis, a single force acts on it. The force is given by , with in meters. The velocity at is .
(a) Find the velocity of the body at .
(b) Find the positive value of at which the body has a velocity of .
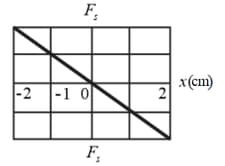
In the figure shown below gives spring force versus position for the spring-block arrangement of in the figure shown below. The scale is set by We release the block at . How much work does the spring do on the block when the block moves from to (a) , (b) , (c) and (d) ?
The block in the figure shown below lies on a horizontal frictionless surface and the spring constant is . Initially, the spring is at its relaxed length and the block is stationary at position Then an applied force with a constant magnitude of pulls the block in the positive direction of the -axis, stretching the spring until the block stops. When that stopping point is reached, what are
(a) the position of the block, (b) the work that has been done on the block by the applied force and (c) the work that has been done on the block by the spring force? During the block's displacement, what are (d) the block's position when its kinetic energy is maximum and (e) the value of that maximum kinetic energy?
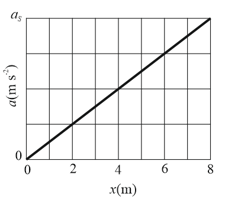
A brick moves along an -axis. Its acceleration as a function of its position is shown in the figure shown below. The scale of the figure's vertical axis is set by . What is the net work performed on the brick by the force causing the acceleration as the brick moves from to ?