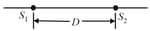A stationary detector measures the frequency of a sound source that first moves at constant velocity directly toward the detector and then, (after passing the detector) directly away from it. The emitted frequency is . During the approach the detected frequency is and during the recession it is . If , what is the ratio of the speed of the source to the speed of sound ?

Important Questions on Waves-II
The figure shows two isotropic point sources of sound and . The sources emit waves in phase at wavelength , they are separated by . If we move a sound detector along a large circle centered at the midpoint between the sources, at how many points do waves arrive at the detector
exactly in phase and
out of phase ?
Approximately, a third of people with normal hearing have ears that continuously emit a low-intensity sound outward through the ear canal. A person with such spontaneous otoacoustic emission is rarely aware of the sound, except perhaps in a noise-free environment, but occasionally the emission is loud enough to be heard by someone else nearby. In one observation, the sound wave had a frequency of and pressure amplitude of . What were
the displacement amplitude and
the intensity of the wave emitted by the ear?
Two loudspeakers are located apart on an outdoor stage. A listener is from one speaker, and from the other. During the soundcheck, a signal generator drives the two speakers in phase with the same amplitude and frequency. The transmitted frequency is swept through the audible range ( to ).
What is the lowest frequency that gives a minimum signal (destructive interference) at the listener's location?
By what number must be multiplied to get
the second lowest frequency that gives minimum signals?
the third lowest frequency that gives minimum signal?
What is the lowest frequency that gives the maximum signal and (constructive interference) at the listener's location?
By what number must be multiplied to get
the second lowest frequency that gives maximum signal and
the third lowest frequency that gives maximum signal?
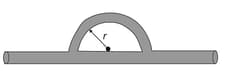
Sound with a wavelength travels rightward from a source and through a tube that consists of a straight portion and a half-circle. Part of the sound and then rejoins the half-circle and then rejoins the rest of the wave, which goes directly through the straight portion. This rejoining results in interference. What is the smallest radius that result in an intensity minimum at the detector?
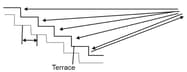
A handclap on a stage in an amphitheater sends out sound waves that scatter from terraces of width . The sound returns to the stage as a periodic series of pulses, one from each terrace; the parade of pulses sound like a played note.
(a) Assuming that all the rays in are horizontal, find the frequency at which the pulses return (that is, the frequency of the perceived note).
(b) If the width of the terraces were smaller, would the frequency be higher or lower?
The crest of a parasaurolophus dinosaur skull is shaped somewhat like a trombone and contains a nasal passage in the form of a long, bent tube open at both ends. The dinosaur may have used the passage to produce sound by setting up the fundamental mode in it.
(a) If the nasal passage in a certain parasaurolophus fossil is long, What frequency would have been produced?
(b) If that dinosaur could be recreated (as in Jurassic park), would a person with a hearing range of to be able to hear that fundamental mode, and if so, would the sound be high or low frequency? Fossil skulls that contain shorter nasal passage are thought to be those of the female parasaurolophus.
(c) Would that make the female's fundamental frequency higher or lower than the male's?