A steady flow of a liquid of density is shown in figure. At point , the area of crosssection is and the speed of flow of liquid is . At point , the area of crosssection is . Between the points and , the pressure difference is and the height difference is . The value of is
(Acceleration due to gravity )
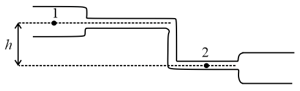
(Acceleration due to gravity )

Important Questions on Mechanical Properties of Fluids
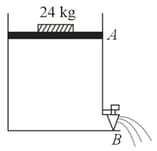
Consider a water tank as shown in the figure. It's cross-sectional area is . The tank has an opening near the bottom whose cross-section area is . A load of is applied on the water at the top when the height of the water level is above the bottom, the velocity of water coming out the opening is . The value of , to the nearest integer, is ___ .[Take the value of to be ]
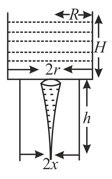
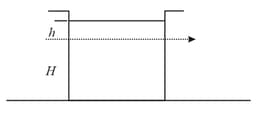
Consider a water jar of radius R that has water filled up to height H and is kept on a stand of height h (see figure). Through a hole of radius r at its bottom, the water leaks out and the stream of water coming down towards the ground has a shape like a funnel as shown in the figure. If the radius of the cross-section of water stream when it hits the ground is x. Then:
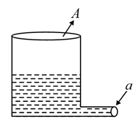
A light cylindrical vessel is kept on a horizontal surface. Area of the base is A hole of cross-sectional area is made just at its bottom side. The minimum coefficient of friction necessary to prevent sliding the vessel due to the impact force of the emerging liquid is
Reason (R): The air currents at the top have smaller velocity and thus less pressure at the bottom than at the top.
A cylindrical container containing water has a small hole at height of from the bottom and at a depth of from the top surface of the liquid. The maximum horizontal distance travelled by the water before it hits the ground is
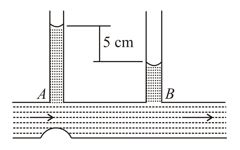
In the diagram shown, the difference in the two tubes of the manometer is , the cross-section of the tube at and is and respectively. The rate at which water flows through the tube is

