EASY
Earn 100
A stone is projected vertically upwards with a velocity of , find the total time taken by the stone to reach the launch point and also calculate the maximum height reached by it.
Important Questions on Motion
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
The velocity – time graph of a moving body is shown in the figure. Which of the following statements is true?
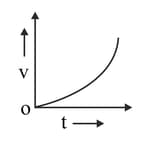
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
Three particles A, B and C are thrown from top of a building with same speed. A is thrown upwards, B is thrown downwards and C is thrown horizontally, they hit the ground with speed , and respectively then
EASY
A particle starts its motion from rest under the action of a constant force. If the distance covered in first 10 seconds is S1 and that covered in next 10 seconds is S2 then
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
Derive third equation of motion by graphical method.
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
Match the first column with appropriate entries in the second and third columns and remake the table.
| S. No. | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
| 1 | Negative acceleration | The velocity of the object remains constant | A car, initially at rest reaches a velocity of in seconds |
| 2 | Positive acceleration | The velocity of the object decreases | A vehicle is moving with a velocity of |
| 3 | Zero acceleration | The velocity of the object increases | A vehicle moving with the velocity , stops after seconds |
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM

