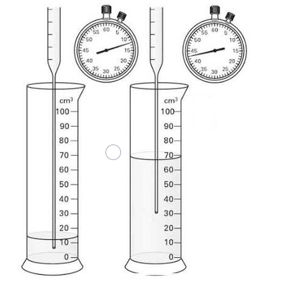
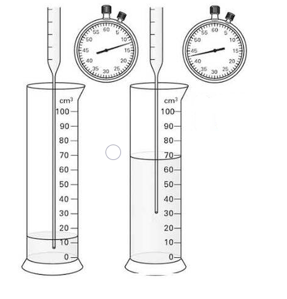
A student collecting water as its runs into a measuring cylinder. She uses a clock to measure the time interval between measurements. The level of the water in the cylinder is shown at two times, together with the clock at these times. Calculate the volume of water collected between these two times.


Important Questions on Making Measurements
A student collecting water as its runs into a measuring cylinder. She uses a clock to measure the time interval between measurements. The level of the water in the cylinder is shown at two times, together with the clock at these times. Calculate the time interval.
A student is measuring the density of a liquid. He places a measuring cylinder on a balance and record its mass. He then pours liquid into the cylinder and records the new reading on the balance. He also records the volume of the liquid.
Mass of empty cylinder
Mass of cylinderliquid
Volume of liquid
Using the results shown, calculate the density of the liquid.
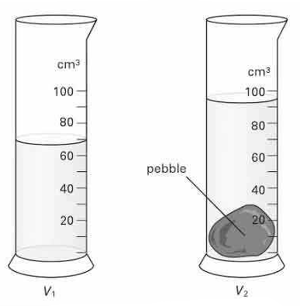
An student thinks it may be possible to identify different rocks and by measuring their densities. She uses an electronic balance to measure the mass of each sample and uses the 'displacement method' to determine the volume of each sample. The diagram shows her displacement results for sample . State the volume shown in each measuring cylinder.
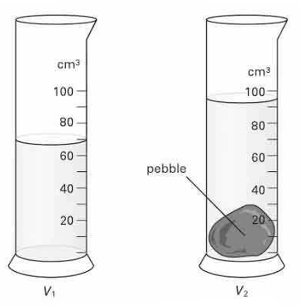
An student thinks it may be possible to identify different rocks and by measuring their densities. She uses an electronic balance to measure the mass of each sample and uses the 'displacement method' to determine the volume of each sample. The diagram shows her displacement results for sample . Calculate the volume of the rock sample .