A student is sitting on the beach, observing a power boat moving at speed on the sea. The boat has a siren emitting a constant sound of frequency . The boat moves around in a circular path with a speed of . The student notices that the pitch of the siren changes with a regular pattern.
(a) Explain why the pitch of the siren changes, as observed by the student.

Important Questions on Waves
A student is sitting on the beach, observing a power boat moving at speed on the sea. The boat has a siren emitting a constant sound of frequency . The boat moves around in a circular path with a speed of . The student notices that the pitch of the siren changes with a regular pattern.
(b) Determine the maximum and minimum frequencies that the student will hear.(Speed of sound in air
A student is sitting on the beach, observing a power boat moving at speed on the sea. The boat has a siren emitting a constant sound of frequency . The boat moves around in a circular path with a speed of . The student notices that the pitch of the siren changes with a regular pattern.
(c) At which point in the boat's motion will the student hear the most high-pitched note? (Speed of sound in air
This diagram shows some air particles as a sound wave passes.

(a) On a copy of the diagram, mark:
(i) A region of the wave that shows a compression-label it .
This diagram shows some air particles as a sound wave passes.

(b) Describe how the particle labelled P moves as the wave passes.
This diagram shows some air particles as a sound wave passes.

(c) The sound wave has a frequency of . Explain, in terms of the movement of an individual particle, what this means.
This diagram shows some air particles as a sound wave passes.

(d) The wave speed of the sound is . Calculate the wavelength of the wave.
In an experiment, a student is determining the speed of sound using the equation . The values of frequency and wavelength are shown below:
Determine the speed including the absolute uncertainty.
This diagram shows a loudspeaker producing a sound and a microphone connected to a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO).
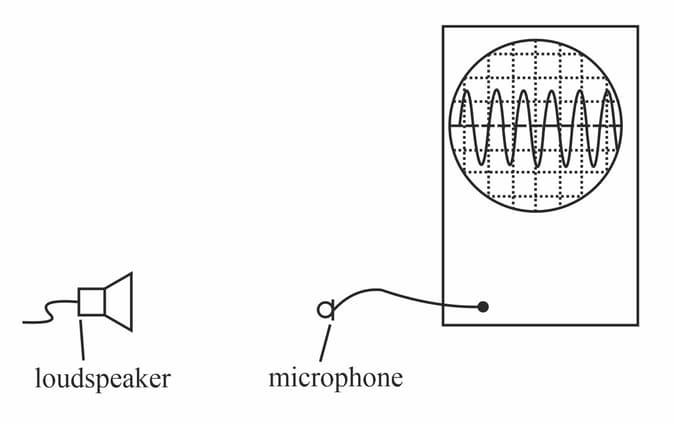
(a) Sound is described as a longitudinal wave. Describe sound waves in terms of the movements of the air particles.
