A student was asked to perform an experiment to study the force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field. He took a small aluminium rod AB, a strong horse shoe magnet, some connecting wires, a battery and a switch and connected them as shown. He observed that on passing current, the rod gets displaced. On reversing the direction of current, the direction of displacement also reversed.
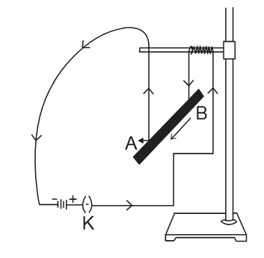
In the above experimental set up, when current is passed through the rod, it gets displaced towards the left. What will happen to the displacement if the polarity of the magnet and the direction of current both are reversed?


Important Questions on Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
"Magnetic field is a physical quantity that has both direction and magnitude." How can this statement be proved with the help of magnetic field lines of a bar magnet?
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown.
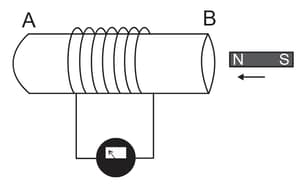
When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards the end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer. A deflection in the galvanometer is also observed when the magnet is held stationary and the coil moved towards the south pole of the magnet. Why?
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards the end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.
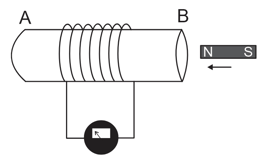
What is a galvanometer? Why does its needle deflects when magnet is moved towards the coil to which it is connected?
