A tank of large base area is filled with water up to a height of . A hole of cross-section in the bottom allows the water to drain out in continuous streams. For this situation, mark out the correct statement(s).
Important Questions on Mechanics of Solids And Fluids
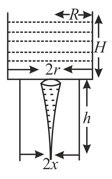
Consider a water jar of radius R that has water filled up to height H and is kept on a stand of height h (see figure). Through a hole of radius r at its bottom, the water leaks out and the stream of water coming down towards the ground has a shape like a funnel as shown in the figure. If the radius of the cross-section of water stream when it hits the ground is x. Then:
(Take )
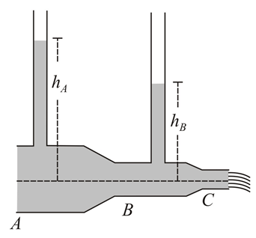
Water flows through a pipe as shown in the figure. The areas of cross-section of sections and respectively are and . The gauge pressure in the pipe at the centre of section is and the flow rate is . The difference in heights of the water levels in the vertical pipes is_____ . (Acceleration due to gravity )
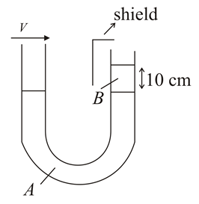
A -tube open at both the ends is partially filled with a liquid of density . Another liquid of density is poured into one of the arms and it forms a column of length as shown in the figure. If the arm into which liquid is poured is shielded from any air motion, the speed with which air should be blown across the top of the other arm till the levels of the two liquids are at same height in is (Density of air is , Acceleration due to gravity )