A test tube contain the acidic radical . If dilute is added in this tube then colourless vapours with smell of vinegar is formed. gives deep red colour on reaction with neutral ferric chloride solution due to the formation of complex ion which decomposed on heating to form (brown-red precipitate). and . respectively are

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Principles of Qualitative Analysis from Embibe Experts Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Chemistry Solutions
1. Charcoal Cavity Test:
|
Observation |
Inference | |
|
Incrustation or Residue |
Metallic bead |
|
|
Yellow when hot, white when cold |
None |
|
|
Brown when hot, yellow when cold |
Grey bead which marks the paper |
|
|
No characteristic residue |
Red beads or scales |
|
|
White residue which glows on heating |
None |
|
|
Black |
None |
Nothing definite-generally coloured salt |
2. Cobalt Nitrate Test:
| S. No. | Metal | Colour of the mass |
| 1. | Zinc | Green |
| 2. | Aluminium | Blue |
| 3. | Magnesium | Pink |
| 4. | Tin | Bluish – green |
3. Flame Test:
| Colour of Flame |
Inference |
| Crimson Red / Carmine Red |
Lithium |
| Golden yellow |
Sodium |
| Violet / Lilac |
Potassium |
| Brick red |
Calcium |
| Apple Green / Yellowish Green |
Barium |
| Green with a Blue centre/Greenish Blue |
Copper |
4. Borax Bead Test:
| Metal | Colour in oxidising flame | Colour in reducing flame | ||
| When Hot | When Cold | When Hot | When Cold | |
| Copper | Green | Blue | Colourless | Brownish red |
| Iron | Brownish yellow | Pale yellow / Yellow | Bottle green | Bottle green |
| Chromium | Yellow | Green | Green | Green |
| Cobalt | Blue | Blue | Blue | Blue |
| Manganese | Violet / Amethyst | Red / Amethyst | Grey/Colourless | Grey / Colourless |
| Nickel | Violet | Brown/Reddish brown | Grey | Grey |
5. Analysis of ANIONS (Acidic Radicals):
(i) Dilute sulphuric acid/dilute hydrochloric acid group:
(a) Carbonate ion :
Dilute test: A colourless odourless gas is evolved with brisk effervescence.
Lime water/Baryta water test:
(b) Sulphite ion :
Dilute test:
; has suffocating odour of burning sulphur.
Acidified potassium dichromate test: The filter paper dipped in acidified turns green.
Barium chloride/Strontium chloride solution:
White precipitate dissolves in dilute .
(c) Sulphide ion :
Dilute test: Pungent smelling gas like that of rotten egg is obtained.
Lead acetate test:
Sodium nitroprusside test: Purple coloration is obtained.
Cadmium carbonate suspension/ Cadmium acetate solution:
(d) Nitrite ion :
Dilute test:
;
Starch iodide test:
(starch iodine adsorption complex)
(e) Acetate ion
Dilute test:
Neutral ferric chloride test:
(ii) Conc. GROUP:
(a) Chloride ion :
Concentrated test:
Silver nitrate test:
White precipitate is soluble in aqueous ammonia and precipitate reappears with .
;
Chromyl chloride test:
;
(b) Bromide ion :
Concentrated test:
;
Silver nitrate test:
Yellow precipitate is partially soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia but readily dissolves in concentrated ammonia solution.
Chlorine water test (organic layer test):
dissolve to give reddish brown colour in organic layer.
(c) Iodide ion :
Concentrated test:
(pungent smelling dark violet)
Starch paper test:
Iodides are readily oxidised in acid solution to free iodine; the free iodine may than be identified by deep blue colouration produced with starch solution.
.
Silver nitrate test:
Bright yellow precipitate is formed.
Bright yellow precipitate is insoluble in dilute aqueous ammonia but is partially soluble in concentrated ammonia solution.
Chlorine water test (organic layer test):
dissolves to give violet colour in organic layer.
(d) Nitrate ion
Concentrated test:
Pungent smelling reddish-brown vapours are evolved.
Addition of bright copper turnings or paper pellets intensifies the evolution of reddish-brown gas.
;
.
Brown ring test:
.
.
(iii) Miscellaneous Group:
(a) Sulphate ion :
Barium chloride test:
.
White precipitate is insoluble in warm dil. as well as but moderately soluble in boiling concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Lead acetate test:
White precipitate soluble in excess of hot ammonium acetate
(b) Phosphate ion :
Ammonium molybdate test:
6. Analysis of cations:
Group 0: Ammonium ion :
Nessler's reagent test (Alkaline solution of potassium tetraidomercurate :
7. GROUP :
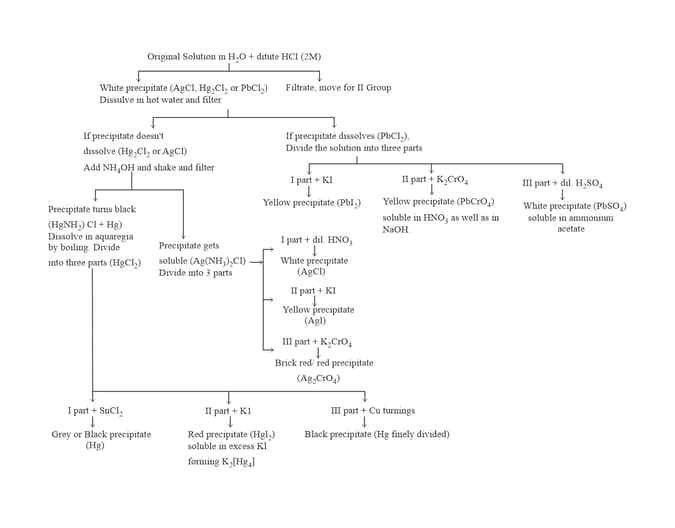
8. GROUP
:
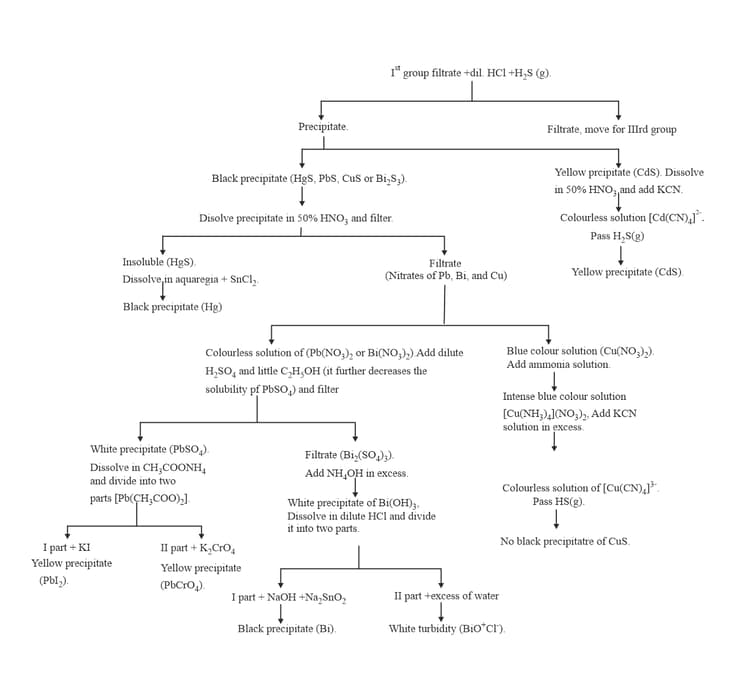
9. GROUP :
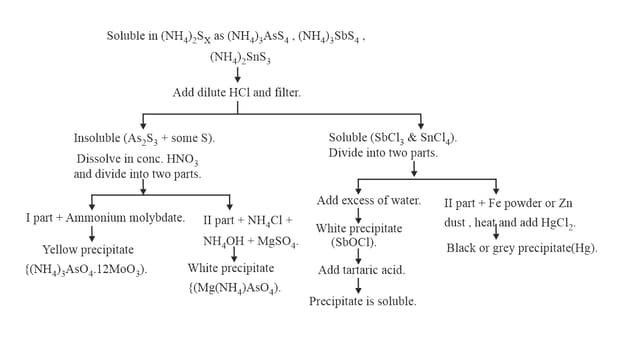
10. GROUP :
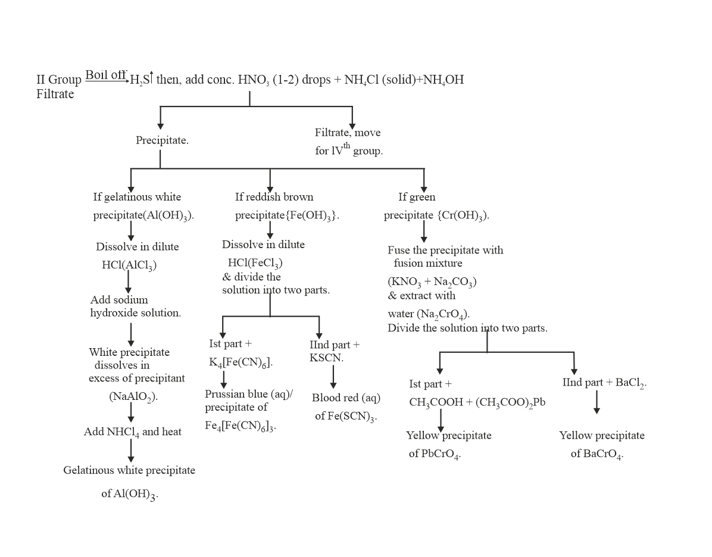
11. GROUP :
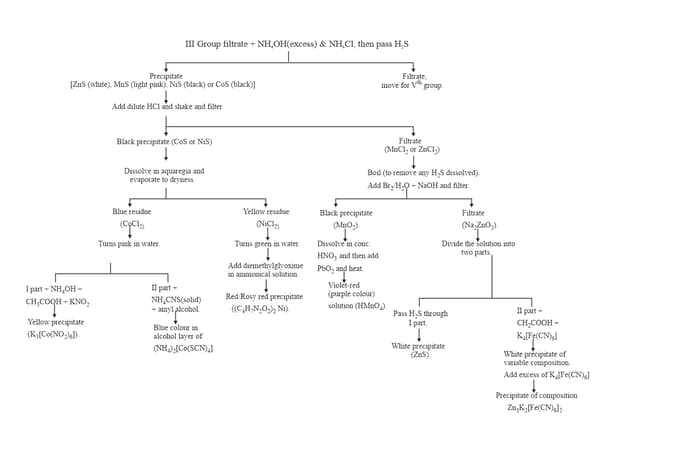
12. GROUP :
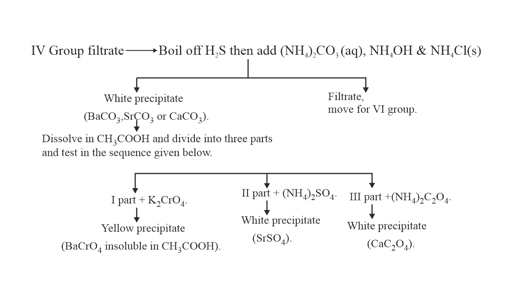
13. GROUP:
(i) MAGNESIUM ION :
(ii) Titan Yellow (a water-soluble yellow dyestuff): It is adsorbed by producing a deep red colour or precipitate.
