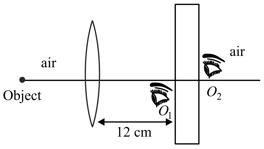
A thin, equiconvex, glass-lens of focal length (in air) is kept at interface of air and transparent liquid. A point object is kept in air at a distance from this interface on optic axis of lens. There is a thick glass plate kept away from lens. In between lens and plate liquid is present. Right to plate air is present. Two observers, and are present very close to optic axis on left and right side of glass plate respectively. Instantaneously speed of the object, the lens and the plate are leftwards, leftwards and rightwards respectively. Take refractive index of glass and of liquid . Instantaneously

Important Questions on Ray Optics
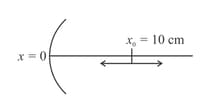
A particle is oscillating on the -axis with an amplitude about the point with a frequency. A concave mirror of focal length is placed at the origin (see figure).
Identify the correct statements?
(i) The image executes periodic motion.
(ii) The image executes non-periodic motion.
(iii) The turning points of the image are asymmetric with respect to the image of the point at .
(iv) The distance between the turning points of the oscillation of the image is .
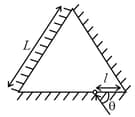
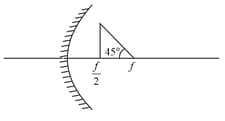
Three plane mirrors form an equilateral triangle with each side of length . There is a small hole at a distance from one of the corners as shown in the figure. A ray of light is passed through the hole at an angle and can only come out through the same hole. The cross section of the mirror configuration and the ray of light lie on the same plane.
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
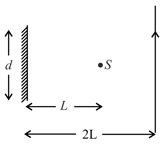
A point source of light, is placed at a distance in front of the center of plane mirror of width which is hanging vertically on a wall. A man walks in front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror, at a distance as shown below. The distance over which the man can see the image of the light source in the mirror is:
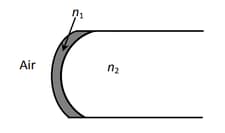
A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index , as shown in the figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distance f2 from the film. Then
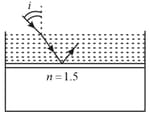
| Column 1 | Column 2 | ||
| (A) | (a) | Convex mirror | |
| (B) | (b) | Concave mirror | |
| (C) | (c) | Real image | |
| (D) | (d) | Virtual image |
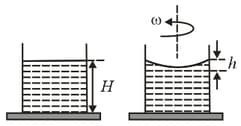
A beaker of radius is filled with water up to a height as shown in the figure on the left. The beaker is kept on a horizontal table rotating with angular speed . This makes the water surface curved so that the difference in the height of water level at the centre and at the circumference of the beaker is , as shown in the figure on the right. Take this surface to be approximately spherical with a radius of curvature Which of the following is/are correct? ( is the acceleration due to gravity)