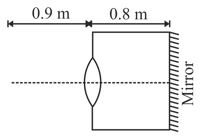
A thin equiconvex lens of a glass of refractive index of focal length in air is sealed into an opening at one end of a tank filled with water . On the opposite side of the lens, a mirror is placed inside the tank on the tank wall perpendicular to the lens axis, as shown in the figure. The separation between the lens and the mirror is . A small object is placed outside the tank in front of the lens at a distance of from the lens along its axis. Find the position (relative to the lens) of the image of the object formed by the system.


Important Questions on Ray Optics
A prism of refractive index and another prism of refractive index are stuck together without a gap as shown in the figure. The angles of the prisms are as shown. and depend on , the wavelength of light according to and where is in .
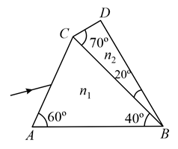
(i) Calculate the wavelength for which rays incident at any angle on the interface pass through without bending at that interface.
(ii) For light of wavelength , find the angle of incidence on the face such that the deviation produced by the combination of prisms is minimum.
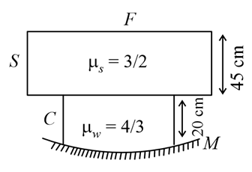
A fly is sitting on a glass slab thick and of refractive index . The slab covers the top of a container containing water upto a height of . The bottom of the container is closed by a concave mirror of radius of curvature . Locate the final image formed by all refractions and reflection assuming paraxial rays.
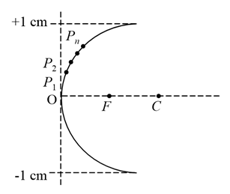
The figure below depicts a concave mirror with centre of curvature focus , and a horizontally drawn as the optic axis. The radius of curvature is and . A ray of light , parallel to the optical axis and at a perpendicular distance from it, is incident on the mirror at . It is reflected to the point on the optical axis, such that . Here is a measure of lateral aberration.
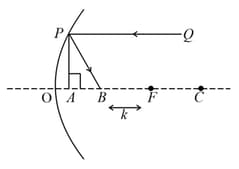
(a) Express in terms of .
(b) Sketch
(c) Consider points on the concave mirror which are increasingly further away from the optic centre and approximately equidistant from each other(see figure below). Rays parallel to the optic axis are incident at and reflected to points on the optic axis. Consider the points where these rays reflected from intersect the rays reflected from respectively. Qualitatively sketch the locus of these points in figure below for a mirror (shown with solid line) with radius of curvature .
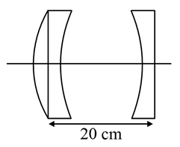
A symmetrical converging convex lens of focal length & diverging concave symmetrical lens of focal length are cut from the middle and perpendicularly and symmetrically to their principal axis. The parts thus obtained are arranged as shown in the figure. Find the focal length of this arrangement.
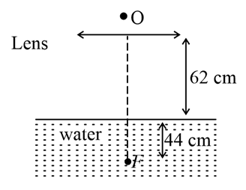
In the given figure, a stationary observer looking at a fish (in water of, ) through a converging lens of focal length . The lens is allowed to fall freely from a the height with its axis vertical. The fish and the observer are on the principal axis of the lens. The fish moves up with constant velocity . Initially, it was at a depth of . The velocity with which the fish appears to move to the observer at is, . Find the value of
A glass rod of the refractive index of rectangular cross-section, is bent into a shape see figure (A). The cross-sectional view of this rod is shown in figure (B).
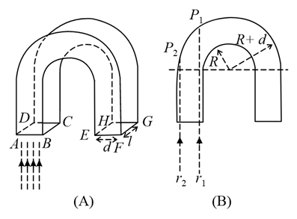
The bent portion of the rod is semi-circular with inner and outer radii and , respectively. A parallel monochromatic beam of light is incident normally on face .
(a) Consider two monochromatic rays and in figure(B). State whether the following statements are True or False.
(b) Consider the ray whose point of incidence is very close to the edge . Assume it undergoes total internal reflection at . In cross-sectional view below, draw the trajectory of this reflected ray beyond the next glass-air boundary that it encounters.
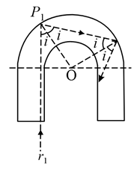
(c) Obtain the minimum value of the ratio for which any light ray entering the glass normally through the face undergoes at least one total internal reflection.
(d) A glass rod with the above computed minimum ratio of , is fully immersed water of refractive index . What fraction of light flux entering the glass through the plane surface undergoes at least one total internal reflection?
